With increasing everyday connectivity and the need for speedy data transfer, copper SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable) transceivers have become integral to the networking architecture. This guide aims to provide a detailed summary of copper SFP transceivers, covering their features, benefits, and use in modern networks. Readers will understand the devices in detail, especially how they help within the needs and budget of a user in terms of data transfer technology, partnering of the devices with multiple types of networking devices, and what to look for while choosing the right transceiver for the right networking job. This guide is suitable for any person trying to develop his/her understanding of networking technologies, whether a network engineer, an IT specialist, or a different user category. You will be furnished with enough information that will help you actively engage in the making of wise choices towards copper SFP transceivers.
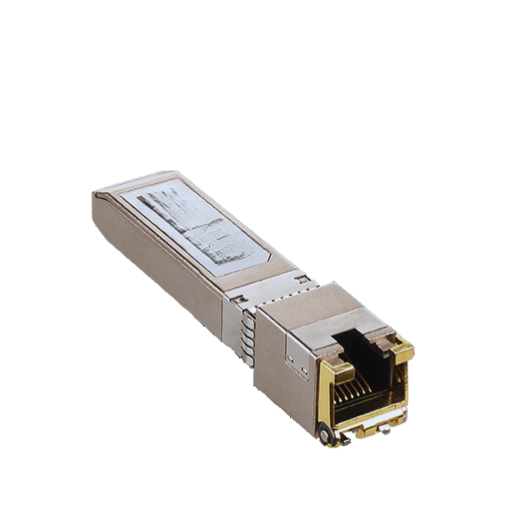

Small Form-factor Pluggable (SFP) transceiver is a small, hot-swappable component used for signal conversion in telemetry and data communication that converts from electrical to optical signals or vice-versa. This includes the whole of the technology that comprises both the transmitters and the receivers that communicate over different data rates, from 1 Gbps-16 Gbps depending on the model and type. Under this category, copper SFP transceivers also use twisted pair cabling systems through electrical signal transport, which enhances connectivity in high speed data networks. They are also made to be stanoctinesan inch and ensure that they can be used together with different networking equipment, which includes switches, routers, and servers. This flexibility in installation has made SFP transceivers a worthwhile and important part of contemporary data communication as they provide room for the growth of networks and upgrading.
Copper SFP modules have several features that have made them preferred by network professionals. First of all, they are economical compared to optical ones, especially on short distances. They cut down the cost implications on both the equipment and the installation. Second, copper SFP modules are easy to set up and configure as they do not need much additional equipment, which helps in efficient deployment and maintenance.
Another demerit that should have been listed here is that the data can be sent over standard Ethernet; hence, it can be used with existing cabling. This, in turn, helps to reduce the costs related to installing new wiring. In addition, most copper SFP modules are designed to have a low degree of latency and a high degree of power efficiency hence attractive for conditions where energy consumption plays an important role. Finally, these modules support high-speed data transmission, allowing optimal efficiency in LAN environments without compromising the safety and reliability of the business processes.
Copper SFP and fiber SFP transceivers have the same intended use in networking but rather perform differently in terms of performance parameters and scope of use. The most apparent reason is the transmission medium; copper SFPs transmit electrical signals via copper cables, which are usually limited to about 100 meters of cables, while the transmission range for fiber SFPs is often several kilometers due to the use of optical fibers.
Likewise, the data rates are different as well as the fiber SFP modules are normally rated for higher data rates than the copper ones which are essential to delivering in environments that need heavy and fast data transfers over long lengths of cables. In addition, copper SFPs are less resistant to EMI interference, which may distort the signal, while fiber SFPs have no interference and thus work well in electrically noisy areas. Bonafide, the copper 100m RJ-45 transceiver module, and bi-directional fiber SFP transceivers are chosen selectively on application parameters such as range, rate, and environmental situation.
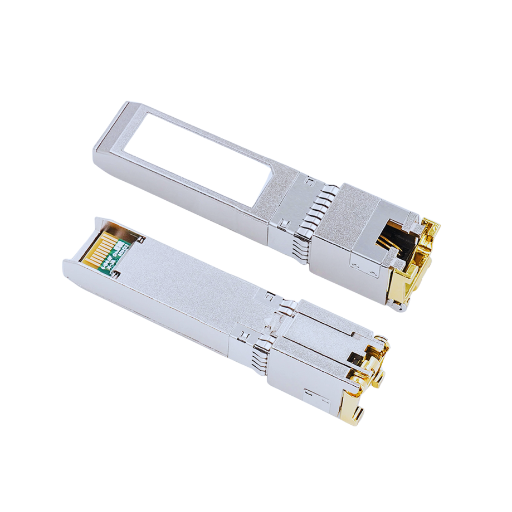

SFP copper modules are made up of a number of elements that are essential to their operation. The transceiver chip serves as the core component of the module, designed to encode all the necessary information into electrical signals, which will be carried over copper. In line with the 10G transceiver chip, potential lower power and enhanced metrics can be supported. Typical 1000Base-T RJ45 connector interfaceThis exposes a very convenient connection to Ethernet ports and also supports multiple SFP transceiver modules.
This circuit board contains all the essential electrical circuitry, including capacitors and resistors, to enhance the modulation and demodulation aspects of data transmission. Additionally, heat sinks may be included to manage thermal output and ensure stability through extended usage. Finally, it is expected to find an EEPROM used with the SFP transceiver modules to enable storage of configuration information. An Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory chip is used for storing fundamental data, such as the module’s characteristics and the device settings, which is needed to help the network identify and work with the module. Knowing such mechanisms and the duplex functionality of fiber optical connections will help in deploying and maintaining copper SFP modules within the networking sphere.
In installing and configuring Ethernet SFP transceivers, many factors have to be considered for the successful adjustment of the equipment and, more so, the maintenance of the network. First, switch off the device, such as a switch and router, before the transceiver is mounted onto it. Then, the SFP module should be placed inside the given SFP slot pipe with a clicking motion confirming it is perfectly held. In the case of copper SFP, the modem’s rj45 socket should be fitted with an Ethernet cable.
After the hardware installation, power on the device and move to the next stage, where configuration will be carried out. Ensure you interface with the management console of the equipment using a web interface or a command prompt and check whether the system detects the installed SFP transceiver. Check out the operating module of the SIP through related commands, such as showing interfaces on the Cisco equipment. Where applicable, do not forget to modify settings to accommodate the purpose of incorporating a connection, for example, changing VLANs or doing link aggregation. It would also be beneficial to test the connection with a network tester after performing the modifications for effective data transmission. Timely supervision of the module’s condition will facilitate the prevention of problems and help enhance network performance.
It should be noted that when dealing with SFP transceivers, especially ones that will be used with Cisco, it is better to understand that Cisco does not endorse any performance issues and generally prefers its own branded modules. Some users turn to third parties because proven methods cost too much and are more desirable than those that are all but guaranteed to fail. Many third-party manufacturers make and sell SFP modules for Cisco-compliant end systems and also theralfetch them on other markets, and all have codvigitalition including terminal passage and Indian verification aggressive.
To avoid any operational incompatibilities, it would be prudent to check the individual model of the SFP against the ICSI SFP compatibility matrix, which contains information for tested modules of various Cisco devices. Further, for devices of another brand, the users need to refer to the brand’s guidelines in relation to the use of SFP modules made by different manufacturers. A transfusion of adaptation typically seeks aid from popular network device manufacturers such as HPE, juniper, etc., but to no avail as these manufacturers have stated which transceivers they recommend for their devices. As a result, through evaluation of both performance specifications and vendor support for SFP transceiver modules, improved performance in network deployment and management may be achievable.
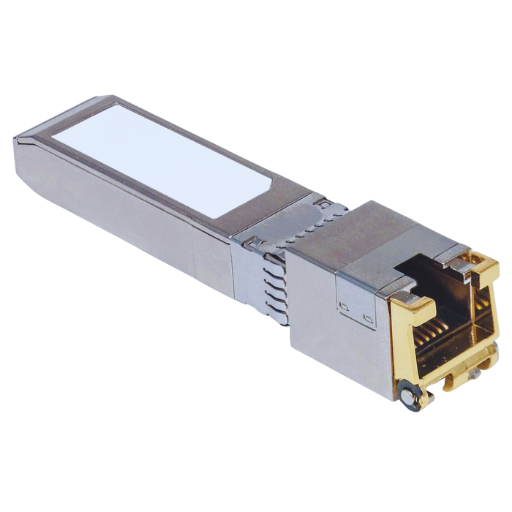

Today, copper 1000base-T SFP modules are practical in data centers since they provide fast data transmission using installed copper wiring. They function at 1 Gbps and are the short-run type, with some distance of 100 meters being the maximum range beneficial for connecting switches, servers, and storage units in the data Centers. Compared to the optical ones, these modules are economically priced and, therefore, suitable for bulk use in areas requiring many connection points. Besides, due to the plug-and-play nature of these devices, the network could be increased using 1000base-t RJ45 SFP transceivers without much downtime as the devices are straightforward to use and expand the network. Their performance is good, and therefore, dependable data is sent, which is very important, especially in the modern day when the data center needs high performance and availability.
The Copper 1000Base-T SFP modules are quite helpful in improving Gigabit Ethernet networks by increasing flexibility and lowering the costs of providing design and deploying portions of the network. They aid in extending the existing Ethernet networks with the same protocols of the usual copper cabling. In this fashion, these modules provide added expected bandwidth by permitting the use of ordinary CAT5e and CAT6 cables for Gigabit rates without the much-quoted struggle for re-cabling or the capital consumption of more expensive optical systems. In addition, their high reliability and low latency elevate the network operating efficiencies and lower system downtimes, hence why they are important for business owners looking at improving network performance. Moreover, in their quest for technology investments that will not be obsolete, businesses will allow Copper 1000Base-T SFP modules to be increasingly desirable where higher speed, lower cost, and higher efficiency are required with the evolution of network architecture.
Copper 1000Base-T SFP modules contribute positively to the network architecture, as routers and switches can utilize those modules. It can also be connected to a router that serves more like a modulator or a pattern router that provides web access and can connect several machines. Switches Copper 1000Base-T SFP modules help allocate the available bandwidth efficiently on the network, thus improving congestion on the local area network (LAN) or efficiently using the available bandwidth. Employing these modules does not interfere with already deployed networking equipment since it is backward compatible, enabling IT managers to optimize performance without swamping any infrastructure. Additionally, the installation and configuration of the devices are simple, which helps in an upgrade of the network, making it easier for an organization’s growth without much training or resources. All in all, modification of the network through Copper 1000Base-T SFP modules integration with routers and switches facilitates its efficiency and reliability.

When it comes to choosing a Copper SFP transceiver, several factors must be taken into account to achieve the optimum performance and the satisfaction of desires on the network.
Having carefully considered these factors, organizations can effectively choose Copper SFP transceivers that satisfactorily address the current networking requirements and lay a foundation for future expansion considerations.
To ensure the best use of Copper SFP transceivers with your network, it is recommended to take the following systematic steps:
Organizations try to increase the compatibility and reliability of the Copper SFP transceiver in the network so that the network’s current and future needs can be met by following the above-mentioned practices.
Most organizations agree that a balance of cost performance analysis for Copper SFP transceivers needs to be indeed presentable, and because of that perform more benchmarks on it so that effective decisions are made that will not compromise performance levels that are critical to the enterprise. The 1000Base-T copper SFP transceivers, which are lower in cost, can be appealing to the clients, but it has apparent disadvantages in terms of reliability, data throughput, and the expected life span. In order to achieve an optimal balance, consider the following:
Organizations can, therefore, mitigate these risks through careful analysis of all these factors and allow for the optimal compromise between performance and cost, thus enabling support for both present and future networking requirements.
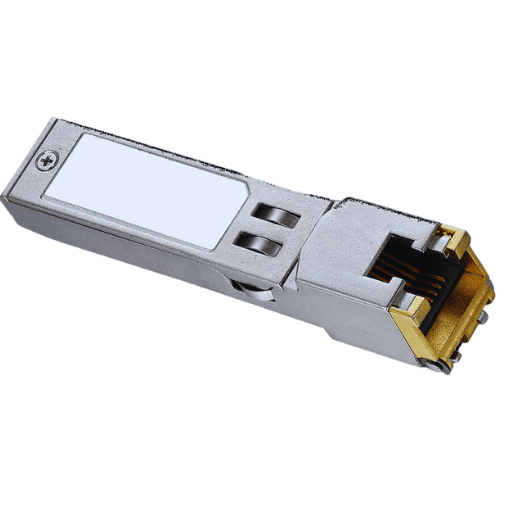

Network functionality can be hampered by connectivity problems involving Copper SFP transceivers, which many factors can cause. Such factors include improper setup, connections that are not suitable, and physical layer problems such as bad cables or connectors. To know how to deal with connectivity problems, follow the tips below:
Network administrators can systematically approach these areas to troubleshoot and rectify the connectivity issues regarding Copper SFP transceivers for better networking.
When troubleshooting any defects of the port and cable in a networking environment, proper orientation is significant. First, ensure that the port under consideration is functional. This is done by checking if the port status indicator LEDs are on. If the port appears faulty, then try to reset the device or perform a power cycle to regain the normal working condition.
After that, examine carefully the specific cables attached to the port. Check for any cuts, sags, or broken connectors. Use the cable tester to check the wiring for the Ethernet cables to make sure the correct pinouts are in place and continuity is maintained. Make sure the cables used can meet the set minimum requirements, such as the marauding of Cat 5e or Cat6 for bandwidth within the network.
Finally, if peering through the channels was awfully on end and a loopback was necessary, troubleshoot the cable and port by looking for a configuration that redirects what comes out of the output to the input again. In this manner, various matters affecting the port and cable can be resolved in due time, thereby enhancing the efficiency of the network system’s operation.
Proper coordination of the firmware and software versions on the networked devices is very important in terms of stability. Network managers must sometimes search for patches from device manufacturers since these patches can eliminate bugs, add new features, and enhance security. To start the updating process, it is advisable to save the current configuration first in order to avoid any data loss. Then, acquire the most current FAG set for the model in question. Be attentive to the release document to see the new or altered features that could have an impact on the current configurations, especially where 10G or copper 100m RJ-45 transceiver modules are to be added.
Once the update is downloaded, it may be necessary to follow instructions provided by the manufacturer for its loading. For example, it may require management software or the application of specific command-line interface protocols. Upon completion of the update, it is important to check the gadget’s functionality to ascertain proper functioning and ensure that all related devices, especially the 1000Base-T RJ45 SFP transceiver module, maintain compatibility. As with computer systems, updating the firmware and the software periodically enhances the whole system’s performance. These practices ensure that the network is functioning optimally and safely.
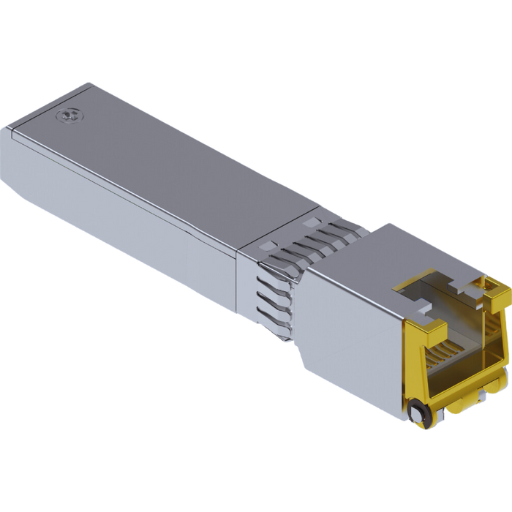
A: A Copper SFP Transceiver is also considered to be a copper transceiver or SFP 1000base-t copper 100m rj-45, is a small size and hot insertable device for network interfacing capable of enabling the transfer of information through copper Rj 45 ethernet connectors. Off the shelf and within a tolerable distance of a hundred meters, this device usually links up devices such as switches and routers.
A: 1000base-t copper is one of the standards used in Gigabit Ethernet over copper cabling. This has a transmission rate of not more than 1 Gbps (gigabit per second), with its transmission medium being UTP cables mostly … connected through an RJ-45 plug, ensuring interoperability with Ethernet.
A: Generally, Copper SFP transceivers adhere to SFP MSA (Multi-Source Agreement), allowing them to work with most network devices fitted with SFP modules. Nevertheless, checking such characteristics with specific devices for normal general operation is prudent.
A: A Copper SFP Transceiver, for example, the 1000base-t copper 100m rj-45 transceiver device, can cover a distance of 100 meters using a normal copper Ethernet cable. This makes them efficient in networking where the distance is short, within a structure or even a small campus, especially while applying duplex fiber patch connections.
A: In connection with 100m RJ-45 transceiver modules, 100m Copper SFPs, and power most often does not go higher than 1.5W, where most of the power is for the clocking end active active module compared to most optical transceiver module types. Nevertheless, timely progress in machinery leads to the creation of dust—and water-proof devices that have emerged as technologies.
A: Copper SFP transceivers include copper ethernet cables and RJ-45 connectors. Therefore, this equipment is never found in fiber optic network networks, where optical transceiver modules and fiber distribution cables are required for perfect operation.
A: When transmitting data over networks, copper SFP transceivers use copper ethernet cables and RJ45 connectors, while optical SFP transceivers rely on fiber optic cables and LC connectors. It is common knowledge that copper modules are limited to a shorter range of about 100 meters; however, optical transceivers involve longer transmitter and receiver ranges and are commonly utilized in high-speed contact network backbones.
A: In the case of a Copper SFP Transceiver, IEEE compliance guarantees that the SFP transceiver meets a well-accepted industry standard such as 1000base-t with the various networking devices consistent and true. Sticking to such guidelines assures a degree of turnover and normal network functioning in situations that adopt the use of fob and copper single and hundred meters RJ-45 transceiver modules.
A: A Copper SFP Transceiver often employs an RJ-45 connector to connect with ordinary Ethernet cables. As a result, it is quite easy and flexible to connect different types of networking devices within a Local Area Network (LAN).