In the rapidly evolving digital landscape, colocation data centers emerge as pivotal infrastructures that facilitate the efficient storage and management of critical data and ensure its high availability and security. These specialized facilities allow multiple tenants to co-locate theicolocate network and storage equipment in a shared environment, offering a cost-effective solution for businesses looking to enhance their IT infrastructure without the hefty investment required to build and maintain their data center facilities. This article explores the multifaceted advantages of colocation data centers, including scalability, reliability, and connectivity options, thus providing a comprehensive overview for organizations considering colocation as a strategy to support their growth and digital transformation initiatives.
Colocation, in the context of data center services, refers to a business model where enterprises and organizations rent space for their servers and other computing hardware in a third-party facility. These colocation facilities provide the physical environment necessary to keep the servers running, including power, cooling, and physical security. Businesses opt for colocation to leverage the economies of scale and advanced infrastructure offered by specialized service providers instead of bearing the capital expenditure associated with constructing, maintaining, and upgrading their data centers. This arrangement not only reduces operational costs but also provides access to higher bandwidth, enhanced security measures, and the resilience of an enterprise-grade data center. In essence, colocation offers a strategic advantage by allowing organizations to focus on their core business activities while relying on expert partners to manage the complexities related to IT infrastructure.
Businesses today face the constant challenge of scaling their IT infrastructure to meet the exponential data processing and storage demand. Colocation data centers emerge as a pivotal solution in this scenario, offering a viable pathway for organizations seeking to expand their capabilities without the enormous financial and logistical burden of constructing and maintaining their own facilities.
Scalability is a core feature of colocation data centers, enabling businesses to rent additional space, power, and cooling as their needs grow. This pay-as-you-grow model provides the flexibility to scale up or down based on current demands, without the upfront investment in physical infrastructure. It is particularly beneficial for companies experiencing rapid growth or those with fluctuating IT requirements.
Furthermore, colocation centers are strategically located to provide optimal connectivity options, ensuring that businesses can maintain high-speed access to their critical applications and data. This connectivity, coupled with the latest in security and compliance standards, makes colocation an attractive option for companies looking to scale efficiently while maintaining high levels of service continuity and data integrity.
In summary, by leveraging colocation data centers, businesses can focus on their core competencies and innovation, knowing that their IT infrastructure is scalable, secure, and supported by specialists in the field. This not only fosters growth but also positions companies to be more agile and competitive in the digital landscape.
The core components of a Data Center Colocation Facility are designed to ensure optimal performance, security, and scalability for housed IT infrastructure. They include:
By integrating these core components, colocation data centers provide a robust, secure, and efficient environment for businesses to house their critical IT infrastructure. This enables organizations to leverage high-grade facilities at a fraction of the cost of building and maintaining their own data center, all while enjoying the benefits of scalability, connectivity, and professional management.
Switching to a colocation provider presents several advantages for businesses seeking to optimize their IT infrastructure management and operational efficiency. Here are key benefits:
By leveraging these advantages, businesses that opt for colocation solutions can achieve remarkable operational efficiency, cost savings, and strategic flexibility, making it an attractive option for organizations of all sizes.
Businesses must consider several key financial and operational factors when evaluating the cost-benefit analysis of colocation versus in-house data centers.
In conclusion, while in-house data centers offer control and potential for customization, the overall cost considerations—both CapEx and OpEx—along with the benefits of scalability, reliability, and access to expert management make colocation an economically attractive option for many organizations.
In the evolving digital landscape, companies are increasingly transitioning away from on-premises data centers towards more flexible, cost-efficient options such as colocation facilities and cloud services. This shift is driven by several key factors:
In summary, the transition away from on-premises data centers is largely motivated by the desire for more economically flexible, scalable, and reliable IT infrastructure solutions. Companies are recognizing the value in freeing themselves from the physical and financial constraints of maintaining their own data centers, choosing instead to harness the benefits of external expertise and advanced technology.
When exploring colocation services, it’s crucial to understand the distinction between retail and wholesale colocation models, as each caters to different business needs and scales.
Retail Colocation is ideal for small to medium-sized businesses that require less space for their IT infrastructure, typically ranging from a single rack to a few racks. Key features of retail colocation include:
Wholesale Colocation, on the other hand, is suitable for larger organizations or those with significant IT infrastructure requirements. This model involves leasing large spaces or entire sections of a data center. Characteristics of wholesale colocation include:
Choosing between retail and wholesale colocation depends on several factors:
In conclusion, understanding the specific needs of your organization and how they align with the offerings of retail or wholesale colocation is essential in selecting the right model. This decision will significantly influence your IT strategy, operational efficiency, and capacity to grow and adapt in the digital landscape.
When evaluating colocation service providers, conducting a comprehensive analysis is imperative to ensure that their offerings align with your organizational requirements and IT strategy. Key areas to scrutinize include:
Choosing the right colocation service provider is pivotal in securing an IT infrastructure that is resilient, scalable, and aligned with your business objectives. An informed decision-making process, underpinned by thorough vetting of potential providers against these criteria, will help establish a robust foundation for your organization’s digital operations.
Understanding Service Level Agreements (SLAs) in the context of colocation services is vital for ensuring that your organization receives the expected level of service and support. An SLA is a contract that outlines the specific services the provider will deliver and sets service performance and availability standards. Here are several key aspects to consider when evaluating SLAs for colocation:
In summary, an SLA is not just a part of the legal contract between your organization and the colocation provider, but a tool for setting expectations and ensuring accountability. A thorough examination of the SLA, focusing on these areas, will help you gauge the fit between a provider’s offerings and your own operational requirements, ensuring a successful partnership.

Physical security measures in colocation centers are a critical component of data protection, aiming to safeguard against unauthorized access, theft, and damage to hardware. These measures include a variety of controls and strategies designed to monitor, detect, and prevent potential physical threats. At the forefront are access control systems, ensuring that only authorized personnel can enter the facility, often employing biometric scanners, security badges, and personal identification numbers (PINs) for verification. Additionally, surveillance cameras strategically placed throughout the premises provide constant monitoring, enabling security teams to oversee activities in real-time and review footage in the event of an incident. Environmental controls are also in place, protecting equipment from extreme temperatures, humidity, and water damage, while fire suppression systems are ready to respond to fire outbreaks without harming the hardware. Together, these physical security measures create a robust defense, enhancing the overall security posture of colocation data center facilities by minimizing the risk of physical threats that could compromise data integrity and availability.
Ensuring data redundancy and reliability in a colocation environment involves implementing strategies that duplicate and safeguard data, guaranteeing that critical information remains accessible and intact even during system failures or catastrophic incidents. Data redundancy is often achieved through methods such as RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) configurations, where data is distributed across multiple disks, and backup solutions, which regularly copy data to a separate storage system to prevent data loss. Furthermore, geographical redundancy, having backup systems located in different physical locations, ensures data availability even if one location is compromised.
Reliability in a colocation environment also hinges on using uninterruptible power supplies (UPS) and generator systems to provide continuous power during outages, alongside network redundancies established through multiple internet service providers (ISPs) and network links to eliminate single points of failure. This multifaceted approach combines hardware, software, and procedural strategies to maintain data’s integrity, availability, and security, ensuring operational continuity for businesses utilizing colocation services. By adopting these measures, colocation facilities can assure their clients that their data and operations are protected against a wide range of potential threats.
In the realm of data center infrastructure, the march of innovation relentlessly advances toward minimizing, if not outright eliminating, downtime. A standout example is the deployment of machine learning algorithms to predict and prevent failures before they disrupt operations. These sophisticated algorithms analyze patterns within vast datasets, identifying anomalies that could indicate impending hardware malfunctions or system failures. This proactive approach allows for the scheduling of maintenance or system replacements during off-peak hours, thereby mitigating potential downtime.
Additionally, the integration of advanced cooling technologies plays a pivotal role in enhancing data center reliability. Overheating is a common cause of equipment failure, and modern cooling solutions, such as liquid or immersive cooling, offer more efficiency and reliability than traditional air-based systems. These methods reduce the risk of hardware failure and significantly lower energy consumption, aligning with the industry’s sustainability goals.
Furthermore, software-defined networking (SDN) revolutionizes how data centers manage network traffic, providing more flexibility and reducing the likelihood of network-related downtime. By decoupling the network control and forwarding functions, SDN allows administrators to dynamically adjust network resources and routes based on real-time demands, thus ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
These innovations, among others, underscore the data center industry’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in achieving near-zero downtime. Through the continuous adoption of cutting-edge technologies and best practices, data centers are well-positioned to meet the evolving demands of businesses in an increasingly digital world.

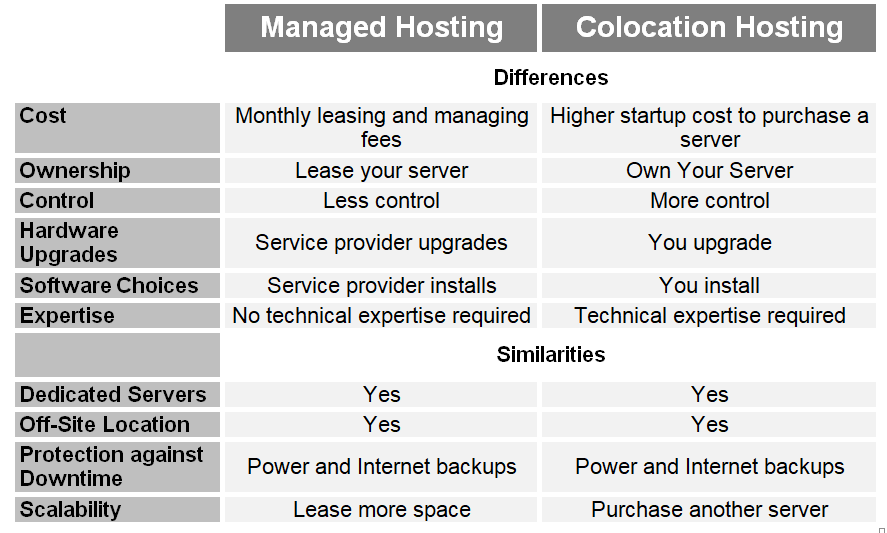
Deciding between colocation and cloud services is a pivotal choice for businesses aiming to optimize their data management strategies while aligning with financial and operational objectives. Colocation, fundamentally, involves renting space in a data center to house your servers and other hardware. This model offers the benefits of advanced infrastructure, improved security measures, and robust connectivity options without the capital expenditure of building and maintaining your own facility. It is particularly appealing for businesses already owning hardware and requiring full control over their server and network configurations.
On the other hand, cloud services provide businesses with virtual resources that can be scaled up or down based on current needs, eliminating the need for physical hardware investments. This flexibility supports fluctuating workloads and can significantly reduce upfront costs. Cloud services also facilitate enhanced collaboration and remote access, making them ideal for companies with a distributed workforce or those requiring extensive data sharing across multiple locations.
The choice between colocation and cloud services hinges on multiple factors, including cost, control, flexibility, and specific business needs. For businesses with existing hardware investments and a need for granular control over their infrastructure, colocation may offer the most value. Conversely, companies prioritizing scalability, remote access, and hardware cost savings should consider the benefits of cloud services. Understanding your organization’s unique requirements and future growth plans is essential in determining the most suitable approach to data management.
Hybrid cloud solutions emerge as a strategic blend of colocation and cloud services, offering businesses the best of both worlds. This model enables companies to leverage their existing hardware within a colocation facility while simultaneously utilizing cloud services’ scalable, on-demand resources. It is particularly advantageous for organizations that face varying workloads, requiring the stability and control of physical infrastructure and the agility to quickly adapt to changing demands.
The technical synergy created by hybrid cloud solutions allows for an optimized IT environment, where sensitive or critical workloads can be managed in-house, while less critical resources can be shifted to the cloud for cost efficiency and scalability. This enhances operational flexibility and provides a failsafe against potential disruptions, ensuring business continuity.
Adopting a hybrid approach also facilitates advanced data management strategies by allowing seamless data movement between private and public environments, optimizing performance and reducing latency in critical applications. For businesses looking to innovate while maintaining a level of control and security over their core assets, hybrid cloud solutions offer a compelling pathway to digital transformation.
Colocation data centers complement cloud service strategies by providing the physical infrastructure for businesses to thrive in a digital landscape. These facilities offer a secure and reliable environment for companies to house critical IT hardware, such as servers and networking equipment, ensuring continuous operation and data integrity. When integrated with cloud services, colocation provides an essential foundation supporting the physical and virtual aspects of a company’s IT strategy.
This synergy enables organizations to maintain a solid operational core within colocation centers while leveraging the flexibility and scalability of cloud services for non-critical functions or additional computing resources needed on demand. This approach reduces the risk of data loss or downtime while allowing businesses to efficiently manage costs by only paying for cloud resources when needed. Furthermore, colocation centers often have high-speed connectivity options that facilitate smooth and rapid data transfer to and from cloud platforms, enhancing overall system performance and user experience.
In summary, combining colocation data centers and cloud services forms a robust framework that supports scalable, reliable, and efficient IT operations. This integrated strategy empowers businesses to deploy a hybrid IT model that aligns with their specific operational requirements and growth objectives.

Maximizing space within a colocation data center is critical for ensuring cost-effectiveness and operational efficiency. One effective strategy is implementing high-density rack configurations, which can significantly increase computing power per square foot. Additionally, adopting aisle containment systems can improve cooling efficiency, thereby allowing for higher density without compromising equipment performance. Regular audits of IT equipment can also identify underutilized resources, providing an opportunity to consolidate and optimize the use of space.
Connectivity and bandwidth are the lifeblood of any IT operation. In a colocation setting, selecting a provider with a rich ecosystem of connectivity options, including direct cloud on-ramps, peering exchanges, and access to multiple internet service providers, is essential. Businesses should also negotiate flexible bandwidth pricing models that can scale with fluctuating demand, ensuring they do not pay for unused capacity while having the ability to ramp up as necessary. Implementing redundant network configurations can further enhance reliability and performance.
Utilizing colocation services can substantially enhance an enterprise’s scalability and performance. By outsourcing the physical infrastructure to colocation providers, businesses can more quickly adapt to growth or changing needs without substantial capital investment in facilities. This agility enables companies to deploy additional resources or expand into new markets rapidly. Strategic partnerships with colocation providers can also offer access to advanced services, like AI and machine learning platforms, further driving innovation and competitive advantage.
These sources were selected for their authority, depth of coverage, and relevance to the topic. They provide a broad spectrum of perspectives, from strategic business considerations to technical operational details and market trends, offering readers a well-rounded understanding of the potential and challenges associated with colocation data centers.

A: The primary benefits of colocation, often referred to as “colo,” in a data center include cost savings on infrastructure, enhanced data center security, access to better network connections, and scalability. Colocation allows businesses to lease space within a data center, providing them with the ability to store their data and systems in a secure, professionally managed environment. This setup helps in reducing data center costs associated with maintaining an entire data center and leverages industry-leading facilities for optimal performance.
A: Data center security in colocation facilities is often more advanced than what most businesses can achieve with their on-premises data centers. Colocation providers invest heavily in security measures including physical security, surveillance, and cybersecurity protocols. This ensures that the space within a data center that hosts data and critical infrastructure is safeguarded against both physical and cyber threats. In comparison, achieving the same level of security may be prohibitively expensive for an individual company managing its entire data center.
A: The main difference between data center and colocation services lies in the ownership and management of the facility. In a traditional data center, the company owns or leases the entire data center and is responsible for its own infrastructure, management, and data center security. On the other hand, colocation services involve renting space in a colocation facility, where the space, cooling, power, and network connections are provided as part of the service. This allows businesses to focus on their core operations while leveraging the benefits of colocation for their data storage and infrastructure needs.
A: There are several types of data centers, including private data centers, public cloud providers, and hybrid cloud-based colocation facilities. Private data centers are fully owned and operated by a single organization for its own use. Public cloud providers offer virtual data center services over the internet. Hybrid cloud-based colocation data centers combine elements of both private and public clouds, allowing businesses to leverage colo data centers for physical infrastructure while integrating with cloud services for flexibility and scalability. Colocation fits into this landscape by providing the physical space and infrastructure needed for businesses to host their private or hybrid cloud environments.
A: When choosing a data center location for colocation, companies should consider several factors including the proximity to their operations, the risk of natural disasters, network connectivity options, and the legal and regulatory environment. Proximity can affect latency and data transfer speeds, while locations prone to natural disasters might require additional considerations for data integrity and disaster recovery plans. Network connectivity and the presence of various ISPs ensure optimal performance, and legal aspects may impact data sovereignty and compliance requirements. Selecting the right data center locations can significantly influence the operational efficiency and reliability of colocation services.
A: Hybrid cloud-based colocation services work by blending the scalability and flexibility of the cloud with the control and security of physical data center infrastructure. Businesses can colocate their critical IT hardware in a colocation facility while also connecting to public cloud services for additional compute resources or applications. This setup allows for dynamic workloads to be managed more efficiently, giving businesses the ability to scale resources up or down as needed. Using a colocation data center as part of a hybrid cloud strategy enables companies to optimize their data center costs, improve data center security, and ensure data and system resilience.
A: In a colocation setting, data center infrastructure management (DCIM) considerations include monitoring and managing power usage, cooling systems, space allocation, and network performance. Businesses must also consider the integration of their equipment with the colo data center’s existing infrastructure, the usage of data center infrastructure management software for efficient operations, and ensuring proper connectivity with internet and data services. Additionally, it is vital to understand the colocation provider’s policies on data center staff access to leased space and equipment, as well as the procedures for adding or upgrading infrastructure components. Effective DCIM ensures optimal performance, efficiency, and security of the data and systems hosted in a colocation facility.