The choice of an Ethernet cable is one of, if not the most critical, decisions when constructing a dependable, high-speed network. Performance-wise, Cat7 Ethernet cables are the most advanced out of all options available on the market. Their unique properties and additional functionality over their predecessors certainly spark a question: “Is Cat7 an optimal choice for my network?”. In this article, I will explain the functionality, benefits, and usage of Cat7 Ethernet cables and why they are often suggested for modern high-bandwidth ecosystems. From upgrading home networks to implementing new data centers, this article is aimed at anyone interested in learning the essentials of the most recent networking innovations and uses.
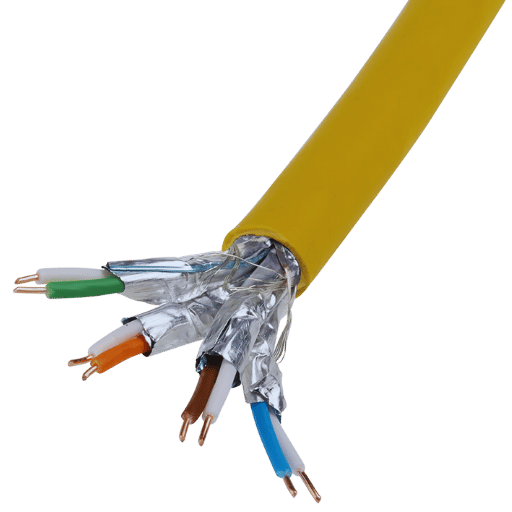
The unique features of Cat7 Ethernet cables are their shielding and superior performance. They have the potential to supersede all previously existing Ethernet cables because they support data transfer speeds of up to 10 Gbps and a bandwidth of up to 600 MHz. The double shielding construction provides interference as well as ensures reliable signal quality even in environments with electromagnetic interference. In addition, Cat7 cables use GG45 connectors that are backward compatible with RJ45 connectors, thus providing versatile networking setup options. These unique properties make Cat7 ideal for very demanding networking requirements.
The electromagnetic interference system, along with radio frequency interference, is one of the major hindering factors of signal degradation. Shielding in networking cables is very important for sustaining signal integrity without distortion in data transmission. For instance, a cat7 shielded foiled twisted pair (S/FTP) networking cable that is double shielded contains an outer braided shield as well as foil shielding around every twisted wire pair. The deployment of such dual-layer shields significantly diminishes the level of external noise, enabling clear signal reception, and also does not allow crosstalk between using adjacent shielded pairs or cables.
Some industry regulations state that Cat seven cables employing braid shields are able to carry frequency signals of up to 600 MHz. This technology enables stable function in high-performance networks where rapid transmission of data is essential. For example, cat 7 cables can provide the speed of transmission of data of 10 Gbps in a 100-meter distance. This functionality makes them highly useful in data centers, server cabinets, and high-tiered residential sets where interferences in signals highly reduce efficiency.
By strengthening the robust shielding materials, the cable’s protection as well as durability is enhanced. These cables are the best suited to function in poorly managed electrically congested environments. Moreover, the double-shielded configurations meet the requirements of ISO/IEC and TIA standards, which lowers the likelihood of incompatibility issues with contemporary networked systems while facilitating technical disturbances.
With knowledge of these shielding methods, different organizations and individuals will be able to select networking cables that align with specific guidelines needed for optimal operational efficiency within a stable communication network.
When compared to Cat6 and Cat5e cables, Cat7 cables hold the superior position. Their data transfer capabilities are remarkable, with an impressive 10 Gbps speed and a bandwidth capacity of 600 MHz, which supports more demanding purposes. The additional shielding that these cables offer minimizes external interference and, at the same time, guarantees reliable connections, especially when there are multiple devices available. Furthermore, these cables are more durable and allow for adaption to advanced networking needs, which guarantees greater value over time.
The performance of Cat 7 Ethernet cables would not be optimal without the use of RJ45 connectors. These connectors blend with the cable’s shield and its twisted-pair conductors, which aids in reducing the possibility of crosstalk or electromagnetic interference (EMI). Unlike ordinary connectors, those used for Cat 7 cables have more robust, shielded designs as these cables have increased shielding.
One benefit of using RJ45 connectors with Cat 7 cables is the ability to accommodate high data transfer rates and bandwidths. These connectors utilize the 600 MHz bandwidth capacity of Cat 7 cables, enabling them to support transmission speeds of 10 Gbps for distances extending up to 100 meters. Furthermore, their high-performance design ensures stable connections, even where network traffic and electronic interference are high.
Moreover, the pin layout within the RJ45 connectors ensures accuracy in data encoding and decoding during transmission which optimizes network reliability. These connectors are backward compatible and able to interface with devices and networks using Cat 6a, Cat 6 and even Cat 5e standards which offer flexibility in mixed infrastructure setups while still maintaining Cat 7 performance.
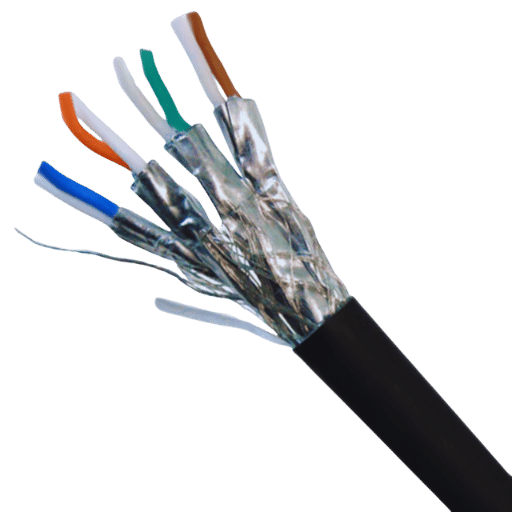

Modern data centers which require fast and dependable connectivity stand to benefit from Cat7 cabling. Offering a maximum distance of 100 meters, the use of Cat7 cables enables the transfer of low-latency data at speeds of up to 10 Gbps. This makes Cat7 cables ideal for high-performance computing environments. Apart from that, Cat7 cables possess an increased bandwidth capacity of up to 600 MHz. This wider bandwidth allows for the transmission of massive amounts of data concurrently without signal deterioration.
Perhaps the primary feature of Cat7 strands is their more advanced shielding. Each pair of wires is foil-shielded individually while the entire cable is protected by additional braid shield. This combination minimizes outer crosstalk and electromagnetic interference (EMI) which guarantees reliability in performance, even in harsh electronic environments.
Cat7 with its Sound infrastructure is more ideal for data centers that deal with cloud services, big data, and Artificial Intelligence workloads as it helps to scale operations with less packet loss and transmission errors. In addition to that, Cat7 improves energy efficiency by minimizing the need for retransmissions which helps ensure stable connections that are necessary to maintain uptime.
Data centers are able to accommodate increasing network traffic and provide unrestricted interconnectivity between servers, storage devices, and networking equipment using Cat7 cabling. Its use in combination with previous standards like Cat6a and Cat5e allow for easy infrastructure upgrades with optimal cost effectiveness and performance.
The enhancement of the Ethernet Systems in the transmission data speed and reduction of the latency time is achieved by the increased bandwidth of the 600MHz, thus making use of the 600MHz bandwidth, and the Ethernet Systems are more efficient. The increased bandwidth facilitates higher data rates, which enables faster and better communication across networks. This is especially helpful to environments with high demand for data, like enterprise networks and data centers where there is a need for consistent performance and low disruption. Moreover, the 600MHz bandwidth guarantees over-the-distance signal improvement, therefore boosting the modern Ethernet connections.
High Bandwidth Capacity:
Support for 10 Gigabit Ethernet:
Improved Shielding:
Extended Reach:
Durability and Longevity:
Backward Compatibility:
Minimal Latency and Maximum Data Integrity:
Energy Conservation:
With a combination of high performance, reliability, and forwarded thinking design, Cat7 cabling is the perfect answer for networks that need 10 Gigabit Ethernet. For such regions, the cabling delivers unparalleled performance and cost-effectiveness. Such enterprises will be able to meet the technological requirements of today while being ready for the emerging innovations of tomorrow.
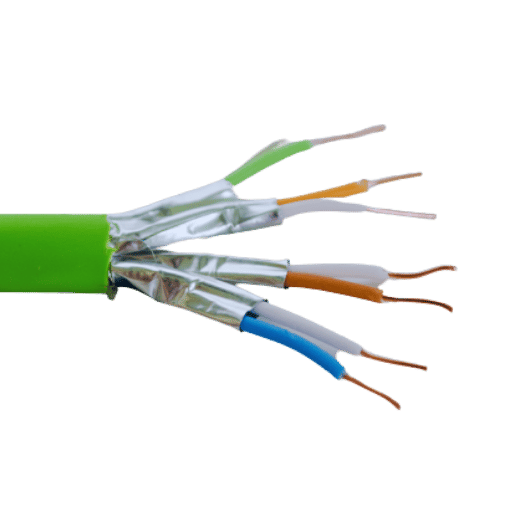
Category 7 cables are crafted to be backward compatible with both Cat6a and Cat5e systems, allowing them to easily plug into existing networks. This ensures that organizations can gradually upgrade their infrastructure without the need of replacing all the cabling at once, therefore optimizing budget and resource allocation.
When interfaced with Cat6a systems, Cat7 cables transmit data at superfast speeds up to 10 Gbps over a distance of 100 meters, as long as the connected hardware supports this standard. Furthermore, Cat7s have better shielding and less crosstalk than the Cat6as, resulting in a far cleaner and more stable signal. These improvements serve the high interference environments well, such as those in industrial facilities or in heavily populated data hubs.
For Cat5e systems, although the maximum transmission speed is restrained to 1 Gbps because of the older standard, Cat7 cables still offer unparalleled durability. The copper-paired shielded cables in Cat7 lessen the electrical interference, thus ensuring data transfer reliability when interfaced with legacy systems.
Additionally, switching to Cat7 cabling will protect the network infrastructure in the future by allowing for the addition of next-generation devices and applications with more demanding bandwidth requirements. This adaptability is what makes Cat7 a pragmatic option for companies trying to optimize their networking solutions for cost, performance, and scalability.
Check to see if the older modems and routers support the standard and connector type of your new Cat7 cables. While Cat7 cables use RJ45 connectors, which most networking hardware is compatible with, older devices may not fully support the higher performance capabilities of Cat7 but will work within their own relaxed limitations. Higher bandwidth caps can be hit with an upgrade in older hardware that would help match modern cabling standards. As always, go through the documentation of the equipment or reach out to the manufacturer to find out compatibility details.
To achieve optimal performance and service life out of Cat7 Ethernet cables, proper handling and installation is of the utmost importance. One such concern is maintaining proper bend radius of the cable. Cat7 cables typically have a recommended minimum bend radius of four times the cables outer diameter. If a cable is bent more than its permitted bend tolerance, it can result in degradation of the signal, reduced transmission speeds, and damage to the internal conductors.
In the same way, maintaining the integrity of the twisted pairs within the cable is of equal importance. Cat7 cables consist of shielded twisted pairs of STP designed to decrease the amount of electromagnetic interference and crosstalk between the cables. These pairs should not be untwisted or stretched too far during installation, or else their effectiveness at shielding will be compromised, which will negatively affect network performance. From untwist limits, industry standards suggest no more than 0.5 inches of untwist near connector terminations.
Consistent management of cables aids in preserving effectiveness. Ensure that no undue force is used while pulling, and avoid any bends or kinks in the middle of the cable. While routing or bundling cables, leave room between the cables to minimize interference while following applicable installation best practices in the ISO/IEC 11801 standards for structured cabling. Not only do these steps guarantee adherence to the performance measurements and thresholds, but they also assist in utilizing the full capabilities of the Cat7 Ethernet network.
Snagless RJ45 connectors have been built to safeguard the locking clip, reducing breakage during cable installation and uninstallation. Their effective use includes the following components:
By adhering to these guidelines, you can maintain reliable connections and prolong the lifespan of your networking components.
SFTP and other shielded cable designs guarantee efficient, high-performance, and robust networking solutions for demanding environments by leveraging these benefits.
As with their specifications, Cat7 and Cat8 Ethernet cables differ with respect to their performance capabilities on bandwidth, transmission speed, shielding and use cases.
Bandwidth:
Data Transmission Speed:
Shielding and Crosstalk Protection:
Application and Use Case:
Cable Length and Limitations:
Certification Standards:
Cost and Availability:
Through these differences, network engineers and IT Professionals may assess if the project would be best served with the use of Cat7 or Cat8 cables, while also ensuring that best operational and economic cost practices are met for each unique case.
Considerations of choosing between a 1000 MHz and 40 Gbps capacity heavily depends on your network requirements and how much change you expect in the future.
Choose the option that meets the operational and financial requirements of the application.
With its potential for high-speed data transmission of up to 40 Gbps, the Cat 8 cable is an exceptional bandwidth-intense application. They also support a frequency of 2000 MHz which provides excellent and dependable connectivity in challenging environments. This makes it highly useful for enterprise networks, data centers, and other high-end performance applications. Their backward istcompatibility with previous ethernet standards enables integration into most existing systems. By investing in Cat 8 cables, you are guaranteed network efficiency while being able to accommodate future technological advancements.
A: It’s worth noting that Cat7, or Category 7, is an advanced series of Ethernet cables built to enhance speed as well as provide superior shielding from electromagnetic interference. Compared to lower categories like Cat5e or Cat6 cablers, they are noticeably thicker and stiffer. Cat7 cables are constructed with bare copper conductors encased in additional shielding, making them ideal for demanding network environments.
A: One of the main purposes of Cat7 Ethernet cables is to increase network performance, servicing speeds of up to 10 Gbps over a hundred-meter distance. Performing at such high speeds, some Cat7 cables are able to accomplish even up to 40Gbps over shorter distances with great ease. Cat7 cables are designed with high Bandwidth applications in mind, which makes these installations a good long-term investment.
A: Indeed, Cat7 Ethernet cables have backward compatibility with equipment designed for Cat6, Cat5e, and even older Ethernet cable versions. Cat7 cables can be utilized alongside the established network infrastructure without running into compatibility issues while also being ready for future improvements.
A: Cat7a is an improvement over Cat7 with even better performance. While the standard Cat 7 supports 10Gbps up to 100m, Cat 7a can accept speeds of 40Gbps over 50 meters and 100Gbps over shorter lengths and has higher specifications for crosstalk and electromagnetic interference.
A: Cat 7 cables perform excellently but may be too much for most home networks today. However, they may be practical for future-proofing a home network when cables are being pulled through walls and with the expectation of higher bandwidth in the future. Most home users find Cat 6 or 6a cables sufficient for their current needs.
A: Like most other types of Ethernet cables, Cat 7 Ethernet cables use RJ 45 connectors. However, some Cat 7 cables use GG45 or TERA connectors, which are proprietary for full Cat 7 performance. Standard RJ 45 connectors will restrict the cable’s performance to those of a Cat6a.
A: Cat8 is built as a superior form of Cat7 with its performance capabilities being significantly better. This shift results in Cat7’s maxed out 10Gbps speed capabilities (or 40Gbps at short ranges) being overtaken by Cat8’s 40Gbps speed over distances of up to thirty meters. Due to greater performance capabilities, Cat8 is tailored for data center applications, thus making it unnecessary for residential or simple small business networks.
1. Design of a Multi-channel PD Detector for Improving Common-mode Noise Reduction Performance in Measuring and Monitoring System
2. Performance analysis for transmission in phantom systems in corporate environments
3. Análise do modo fantasma aplicado a sistemas G.fast e XG.fast
6. Ethernet