During an age where one needs to have reliable and high-speed internet, it becomes necessary that we know about Ethernet cables. The main objective of this article is to explain Cat 6 Ethernet cables in a simple way by pointing out its main features and what makes it better than others like Cat 5 or Cat 5e. We shall cover everything from technical specifications through installation considerations up to performance metrics, thereby giving you all the details that will enable you to make informed decisions for your network infrastructure, Whether as a technical personnel who wants to upgrade his system or just a user interested in improving efficiency at home networks, this guide will help you understand why should someone consider using Category Six cable over any other when they want better connectivity standards.

In comparison to previous models, cat 6 Ethernet cables are built to be faster and have more flow. For example, these cables can transfer data at 10 Gbps over a distance of up to 55 meters because it has a bandwidth capacity of 250 MHz. The reason why they perform better is that the wires within them cross less frequently with other wires which leads to less interference from electrical systems around it thus ensuring a cleaner signal. They can also be used for professional networking environments due to their durability and better protection against crosstalks.
When you compare Cat 6 and Cat 5e Ethernet cables, there are a few key specifications that show how much better Category Six is than Category Five enhanced. Below is a short analysis that looks at the main differences between them:
Bandwidth Capacity:
In data intensive applications where information needs to be transferred very fast, cat six can handle more than double the amount of data that cat5e can hence making it possible for these kinds of apps run smoothly.
Data Transmission Speed:
The modern-day communication systems require high speed internet connections which support atleast one gigabit per second speed. However, some of them may need more bandwidth than others depending on their size hence making category six ideal because it ensures faster communication speeds between devices connected on same network.
Crosstalk and Noise Reduction:
Interference can cause loss of signal quality in transmission lines therefore wires should be properly insulated or shielded from electromagnetic fields created by other nearby cables also known as “cross talk”. Category six has got this feature incorporated into its design thus reducing interference significantly compared with other types such as cat5e.
Physical Structure:
Category six cables have a thicker outer covering called jacketing material, which protects them from physical damage, such as being stepped on or crushed by heavy objects. Moreover, they contain an additional number of twists within an inch, increasing overall durability. Thus, these wires are perfect for outdoor applications where they are exposed to harsh weather conditions such as rain and sunlight.
In light of these technical yardsticks, one can confidently argue that cat6 cables are indeed faster and more reliable than their cat5e counterparts. Therefore if you want your network to be efficient go for the former especially when dealing with big office buildings or residential areas where there are many users simultaneously accessing internet services.
As technology develops, there is an increasing need for data transmission speeds to improve. This growth has been accompanied by a corresponding decrease in latency. Given that bandwidth is often considered the determinant factor of performance and efficiency in Cat 6 cables, its importance cannot be overstated. With a capacity of up to 250 MHz, this type of cable can adequately meet modern requirements, which are characterized by higher demands on data usage, such as HD video streaming or large file transfers, among others. In other words, these cables were made for heavy-duty applications where lots of information must flow through them within very short time periods, like gaming sessions involving multiple players who may also be located far away from each other geographically speaking. The only way such a thing would work out perfectly well without any hitches would be if it had enough bandwidth – so that everything could pass through smoothly simultaneously without having to wait for each other at any point along their paths! There’s no doubt about this fact either: increased bandwidth allows more number users or devices to be able to be used concurrently without experiencing any noticeable lag whatsoever, hence making them the perfect choice for both residential and commercial buildings alike since they help cater to both types of networks easily without requiring much effort from anyone involved including those installing them.

The main difference between Unshielded and Shielded Cat 6 Cables is their construction and application environments.
In short, UTP Cat6 is usually good enough – and cheaper – for homes and offices, but if you’re running cable near fluorescent lights or other strong sources of electrical interference, then go with STP.
Various technical parameters help differentiate Cat6a and Cat 6 Ethernet cables:
To sum it up, CAT6 should work well enough for average homes or offices where networks aren’t too demanding, but if you need more speed or less interference, among many other things, then go with CAT-Seven-A!
Category 6 (Cat 6) cables are very useful in networking environments. For one, they can support up to 1 Gbps of data transfer speeds, which is good enough for most homes and businesses. Alongside this, Cat 6 cables also have a frequency range that can go as high as 250 MHz, which means that they are capable of transferring large amounts of information quickly with little delay. Cost-effectiveness is another major advantage; not only do these cables offer satisfactory performance levels for typical needs, but they are priced reasonably, too – ideal for setups where there is only moderate demand on the network. Another thing about category six cable is its ability to provide shielding against interferences between different wires or signals being transmitted through them, therefore ensuring stability as well as reliability when it comes to connectivity. In general terms, however, what sets these types apart from others is their ability to balance between price and quality because cheapness alone cannot always guarantee robustness, especially in multi-purpose scenarios like networking where expensive options might also fail due to lack of features required by those particular tasks.
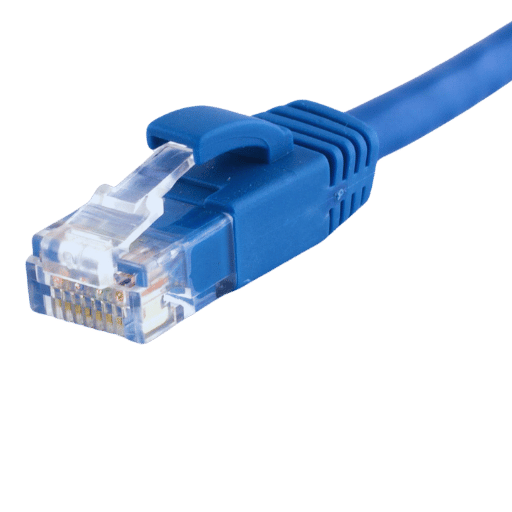
Cat 6 cables also known as Category 6 network cables are a twisted pair cable type designed for Ethernet and other network physical layers. They can offer data transfer rates of up to 1 gigabit per second and operate at frequencies up to 250 megahertz. In this case, the Cat6 cable has stronger requirements on crosstalk and system noise than its predecessors which makes it perfect for areas with unstable connections that require reliable connectivity such as schools or offices. While being applicable in homes where people need moderate size networks as well as businesses where there may be heavy usage but not too much traffic flowing through them at once; these cables will work best when used between devices located within close proximity because they provide an excellent balance between cost and performance.
Unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables are frequently used in settings with minimal electromagnetic interference (EMI) or crosstalk. This type of cable is best for common network needs among home and small business users. Below are the pertinent considerations and technical specifications when deploying UTP cables:
Cost-effectiveness: In general, UTP cables are cheaper than shielded ones, so they’re often chosen for budget-friendly installations.
Ease of use: UTP cables weigh less and can be bent more easily, making them less cumbersome to install. They also don’t have extra layers of shielding that add bulk to the cable and harder to handle.
Compatibility: Because of their widespread usage, UTP cables work with most networking hardware, allowing seamless integration into existing systems.
Performance: UTP cables can handle data transfer speeds up to 1 Gigabit per second (Gbps) and operate at frequencies up to 250 Megahertz (MHz), similar to what Cat 6 specifies. These numbers satisfy typical residential and business requirements.
Examples:
While unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables do not offer as much protection against outside influences as shielded ones do, their mix between cost, ease-of-use, and performance makes them very versatile for most standard networking applications.
If you want high-performance Gigabit Ethernet cables, then there are a few key things to think about:

Design Your Cable Run:
Gather the Necessary Tools and Materials:
Prepare Your Cables:
Connect the RJ45 Connectors:
Check Cable Functionality:
Put Up The Cables:
By doing this, you will have succeeded in installing category six ethernet cables that not only guarantee high performance but also reliability on any network.
To ensure maximum network performance, it is important to maintain the efficiency of Cat 6 Ethernet cables. Here are a few things you can do:
Proper Cable Management:
Electric Interference Prevention:
Sustaining Ideal Ambient Conditions:
Regular Testing & Checking:
Right Way To Install:
By following these maintenance suggestions along with good practices; you can make sure that your cat six ethernet stays efficient while still keeping up high-speed network connectivity anywhere on earth!
Cross-Talk:
Poor Termination:
Bending the Cable too much:
Incorrect Lengths of Cable:
Environmental Impairments :
This is how you could maintain integrity as well as efficiency in your Ethernet installations using CAT 6 cables.

What differentiates Cat5e cables from Cat6 cables are their performance and build. For example, in comparison to Cat5 cables, which was an improvement, Cat5e can facilitate data transfer speeds of 1 gigabit per second over a 100 megahertz bandwidth. On the other hand, these types of wires can only allow high frequency signals up to 250MHz while supporting rates up to 10Gbps within small distances that are between two points not far apart from each other; besides this, they have more twists tightly wound together as well as better insulations so as to minimize crosstalk among adjacent pairs thereby enhancing signal quality during transmission along with reducing electromagnetic interferences thereby making them more reliable in terms of transmitting signals.
Cat 6 cables are best for Gigabit Ethernet because of better technical specifications. These are the main ones:
Technical Facts:
By doing so , we can realize stable , reliable and fast data transfer in networks using these cables thus leading to better performance of applications based on gigabit ethernet.
It is important to identify real Category 6 (Cat 6) cables as this guarantees the best network performance and reliability. Here are the main steps that will help you determine if a Cat 6 cable is genuine:
With these tips at your fingertips, it is possible for one to easily differentiate between what qualifies as original versus counterfeit category six cables while ensuring all high speed reliable data transmission needs are met in a company’s network infrastructure setup.
A: A cat6 ethernet cable can be defined as a LAN cable that performs highly in Gigabit Ethernet and other network protocols. It has higher data transfer speeds than the others and works at a frequency of up to 250 MHz, which reduces crosstalk and makes Ethernet networks more efficient.
A: Several advantages come with using Cat 6 Ethernet Cable, such as better interference protection because of its tightly twisted pair construction, faster data transfer rates, and also support for 10-Gigabit Ethernet over distances of up to 100 meters. Additionally, this type of cable is compatible with previous versions like the ones mentioned above.
A: Yes, cat-6 may be used for both short-distance cable runs and long-distance ones. It can go the same speed but also go further up to one hundred meters long, making it an ideal choice for several networking needs within a room or building.
A: These cables are designed specifically to reduce interference caused by crosstalk through their tighter twisted pair construction which isolates signals. This leads to high-quality signals, hence fast communication, therefore enhancing its reliability as a connection point that is very crucial, especially when dealing with bulk transfers.
A. Yes, they are different; cat-six patch cables are shorter pre-terminated cables usually used to connect devices to a patch panel or router, while on the other hand, bulk cables, being usually longer, are used in permanent installations inside walls or ceilings thus enabling custom lengths based on specific requirements of ethernet network.
A: Yes, Cat 6 Ethernet Cable works with older developments such as Cat 5 and Cat 5e. That means that you can just add Cat 6 to an existing network without having to replace the previous standard compatible devices.
A: At a frequency range of up to 250 MHz, data transfer rates are faster, and signal integrity is more reliable compared to earlier standards. This is crucial for today’s high-speed networks in applications that require fast reliable communications.
A: Typically, RJ45 connectors are used with Cat 6 Ethernet Cable because they are specifically aligned with the cable’s superior performance specifications. They ensure proper signal alignment and reduce loss.
A: Yes, there exist some particular types of outdoor or direct burial oriented cables that fall under this category. Normally these cables have protective jackets that can withstand environmental changes thereby making them suitable even when exposed over time without compromising on their functionality level.
A: By employing higher frequencies and reducing signal loss due to crosstalk through its innovative structure, CAT-6 enables the speed of a Ten-Gigabit Ethernet. As a consequence, more reliable data transfer at rates that do not go beyond fifty-five meters for ten-gigabit applications supports a longer distance than for any other similar product because Gig-Ethernet products do not perform this way.