The C13 socket outlet is the kind of electrical connector used in all electrical equipment and participates actively in the power distribution mold. It is primarily available in computer systems, other professional audio-visual equipment, and even data centers, and this multi-purpose outlet can be used for different devices that need power. The purpose of this document is to shed light on the C13 power socket, which is quite common, its design characteristics, areas of use, and safety measures and precautions taken while using it. Suppose you are a computer technician, electrician, or anybody interested in how this fundamental component of modern technology works. In that case, this article will give you the fundamentals you require to work with and ideally use the C13 outlet.

The field’s most important, IEC 60320, defines the safety and performance requirements of connectors used mainly for connecting domestic and commercial electrical appliances. IEC standards provide design specifications for power cords and connectors, which must be used together to remove power from or supply power to the different equipment. In other words, the C13 socket is one of the C-class network connectors. It regulates parameters such as electrical ratings, temperature ratings, and devices’ mechanical performance. IEC 60320 helps improve product safety by eliminating the likelihood of electric shocks while at the same time promoting the international harmonization of power connectors, facilitating convenient integration of electric systems in many devices for both users and manufacturers.
C13 power sockets, especially information technology and audio-visual settings, are used in many areas. They are typically used in data centers for electronic devices, including servers, network switches, and storage devices since they can deliver ten amps at 250 volts. C13 power sockets are often used for powering monitors, projectors, and other equipment in professional art configurations where a stable power supply for power-consuming devices is needed. In addition, most of these devices are industry-standard interfaces that can be used with many devices in both business and industrial environments.
Differentiating between C13 outlets and other socket outlets, such as C14 and 15, entails some noticeable features. The C14 connector is a reversible in-device power inlet socket, which makes it possible for the device to be powered from the socket through the C13 connector. Its maximum electrical ratings are about the same as C13, but it has a little variation in shape, which enables an optimistic locking with the C13 plug, thus improving its stability. Alternatively, the C15 socket, which has a high-temperature rating, is typically used in high-density installation servers that work under high load conditions; it has a management cut-out that eliminates general C13 plugs.
The C19 outlet is rated to carry 250 volts and 16 amps. It swiftly catches in the data center, where a high-density computing apparatus is used in installations where a high level of power distribution is needed. Although practicality considers the need for all those sockets in the most efficient delivery of electric power, the intersection selection mainly depends on the equipment specifications to be interfaced, power levels, and environmental conditions, among other things.

Choosing a proper C13 power cord also helps to know the different plug types and their configuration and standards, which guarantees that the target devices will easily accommodate the plugs. The C13 plug, which happens to be the most widely used plug configuration, is equipped with three pins that are arranged to optimally serve the electrical needs of a standard computer, router, or hub hardware. Moreover, among other requirements, the general length and temperature rating of the cord or gauge should also be taken into consideration, depending on the application. For example, high gauge cords with few turns are said to be suited for heavy current-rated devices to prevent voltage drop. In contrast, longer cords that do not use the proper ampacity rating may damage or undermine the reliability of the cable and the user’s device. If these parameters are taken into account, it will be easy for the users to know where to procure the electrical power cords, thus improving the use and service of the devices.
To ensure efficient working of electrical equipment, the voltage and ampere ratings must also be closely monitored during power cord selection. The standard voltage of the C13 power cord is about 250 Volts, but this value continuously varies from manufacturer to manufacturer. The C13 connectors’ ampere ratings are about 10 to 13 amps, but there are higher-rated current connections in other configurations of the C19 outlet. However, a proper balance must be done between the needs of the appliance and these ratings; use of such cords that have too low a rating level can result in overheating and burning out of complex electrical equipment; on the other hand, using cords that can take more rating than practical can lead to various inefficiencies and lower equipment lives. It is better to emphasize the importance of matching power cord cut-outs and parameters like voltage and ampere when powering any device to prevent draughts and safety issues concerning any pleasant electrical fragmentation.
Not only can length and gauge (AWG) dictate how well a power cord performs, but it also determines its operating safety. The measurement unit for a wire is the American wire gauge system (AWG), where the lower the value on the gauge, the thicker the wire, which has less resistance and can carry more current without overheating. For power cords, standard AWG ratings are 16, 14 and 12, here 16 gauge is applied on small weight and general use applications while 12 gauge is reserved for high power uses including in a modular system. Their length also has a role in performance; if cords are too long, they might induce a voltage drop and hamper the efficiency of the appliances using such cords. To prevent these problems as much as possible, the user is advised to select the length and type of power cord according to the power that this equipment consumes. In addition, shorter and thicker cords are helpful when cords tend to be pulled more often in high-performance performances.
While selecting a power cord, it is necessary to keep in mind the total distance of the power source to the device and the power rating of the device in question. For example, a 25-foot 14 AWG cord can be used on parts which need up to 15 amps, however on 50-foot 16 AWG cords, although devices which have a lower amperage application can be plugged in for safely and efficiency purposes.
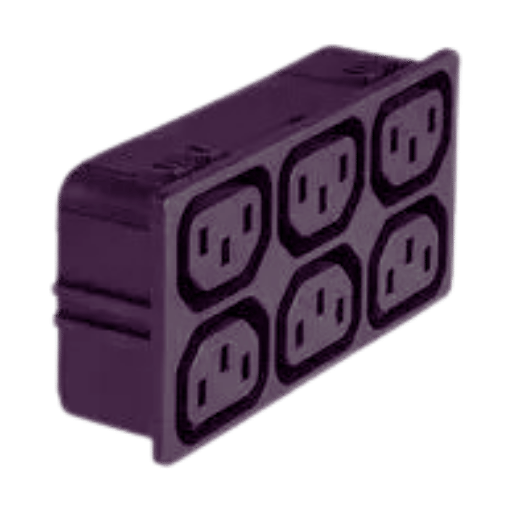
Some procedures must be followed when connecting a PDU with a C13 outlet so that the installation can be carried out safely.
By carrying out these procedures, electrical safety and the proper functioning of your connected devices through the PDU will always be guaranteed.
To make electrical maintenance safe and secure, following safety regulations and standards like those of Underwriters Laboratories (UL) is vital. UL certifications are given only to products that meet the specific indicated criteria. This lessens the defalcation risks and failure due to electric fires. The following safety measures should be considered while installing a C13 outlet:
By following these guidelines, you will ensure the safety, legality, and efficiency of your electrical installations, reducing the chances of losses and ensuring a safe and secure working environment.
While assessing the functionality of both panel-mount and rack-mount installations, one should consider their context, the space they occupy, and the procedures involved in the installation.
To sum up, the selection of either panel-mount or rack-mount installations will be determined by factors such as the space, position, and functional requirements of the machines being installed. Each of the alternatives has its disadvantages and strengths, which make them appropriate for various conditions in electrical installation works.
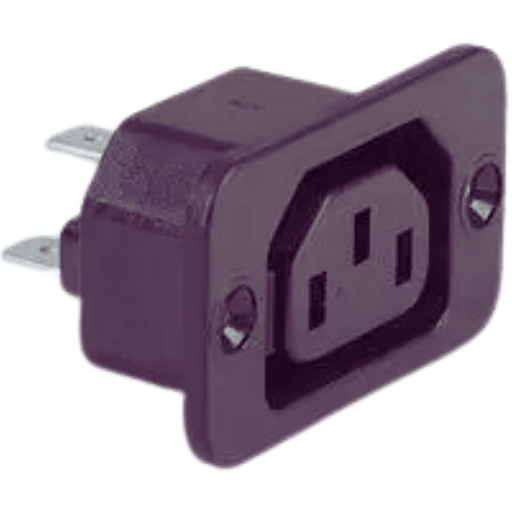
Utilizing a C13 outlet in a data center brings several benefits that optimize power usage. First, the C13 outlets are universal and can be used to connect various IT equipment, such as servers and network switches, reducing the power distribution’s complexity and enhancing its efficiency. Second, such outlets allow standard IEC power cords to be used, making it easy to manage the cables and clutter within the rack. Thirdly, the c13 outlet is usually rated for high currents of about 10Amps – 250Volts, insufficiently limiting equipment that would need uninterrupted dependable supply without chancing an overload. Besides, due to their common usage, integration, and expansion to other existing structures become more accessible, thus making it practical to embrace these C13 outlets to optimize energy consumption in data center operations.
The C13 socket also demonstrates high fidelity with various interchangeable plugs, sockets, and cables, which is crucial to constructing power distribution systems. The C13 is a socket outlet that conforms to the standard IEC 60320 and uses other IEC components, such as C14 plug-ins and connected devices like a server or UPS system. This makes it possible to connect powering equipment that does not require elaborate connectors or adapters, which helps improve efficiency.
Concerning NEMA components, one should remember that there are cases where NEMA connectors, e.g., NEMA 5-15, do not connect with the C13 socket. For example, many dry coolers’ data center designs include IEC and NEMA curved contacts. Using portable PDUs with both available sockets can overcome this problem and allow the mixing of different kinds of equipment without losing safety and performance. This potential is not only provided in the current infrastructure but also allows for the growth of this potential in the future, and it is one of the critical factors in the design and operations of the data center.
Considering the sensitive nature of the equipment and services provided here, one must pay particular attention to ensuring a constant supply of AC power to data center operations. Major ways to achieve these reliability measures include adopting redundant systems, employing uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), and using advanced monitoring system solutions.
Using these strategies, data centers can significantly improve the reliability of their AC power supply, guaranteeing the uninterrupted provision of critical services.

Routine examination and tests of C13 outlets are definite requirements for the safe and effective operation of the facilities. It is also good practice to thoroughly examine the C13 outlets for abrasions, breaking, melting, and other possible over-tempering at the joints. There should also be a determination of continuity and load using the appropriate apparatus of suitably qualified personnel, bearing in mind that the outlets should not be starved of current in operation. It is also helpful to keep these investigations in a regular cycle, for instance, six-monthly, as this may help detect problems earlier before they get out of control. Making a record of the performance of the inspections and the outcome of the inspection is crucial as it will help to avoid violating safety regulations and also for periodic evaluation.
It is essential to replace damaged or worn cords to maintain the safety and practicality of the C13 outlets. When a cord shows signs of wear, such as cracks, frays, or discoloration, it should permanently be changed at once to prevent any chances of electrical fire. The replacement procedure involves the following steps:
Changing the cords on a regular basis as a maintenance activity also reduces the chances of accidents, which would result in equipment breakdown or fire hazards. Thus, operation within the data centers or any electrical installation is not disrupted.
To calculate the environmental and loading conditions for the C13 outlets and all the associated components, it is necessary to consider a few elements:
Handling these elements adequately enables organizations to minimize the risk of electrical failures greatly and, therefore, increase the safety and efficiency of their electrical installation overall.
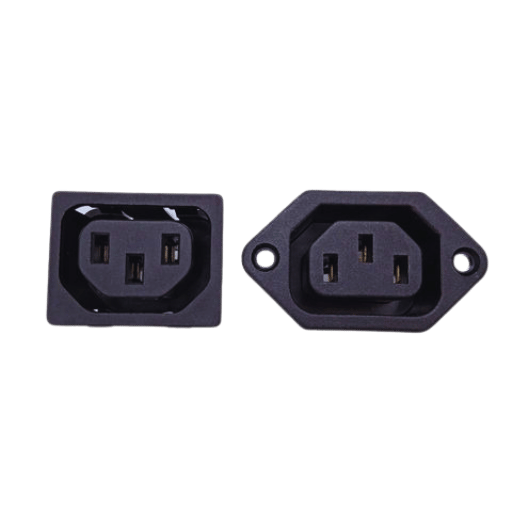

The C14 to C13 adapters are meant only for conversion of the C13 connector to the C14 connector to permit devices with C14 plugs to be plugged into C13 sockets. These adapters are incredibly convenient when servers or power supplies having C14 ends need to connect to the existing C13 socket infrastructure. An adapter being procured must be rated to match the specifications for voltage and current, usually about 10A at 250V, under stipulated standards, which are pretty relevant. Further, the users of such adapters should check the product’s certification and quality to prevent overheating or electric damage when using Schuko plugs. It is recommended that the technical parameters of the adapter and the appliances with which it will be used be looked up.
NEMA 5-15P plug adapters are designed for use with appliances equipped with NEMA 5-15R inlets, plugging them into standard 120V operations. Such adapters make it possible to “plug in” a wide range of electronic equipment, such as computers and home devices, to the power grid without redoing the wiring. In choosing a NEMA 5-15P adapter for your device, one must determine the device’s power specifications and requirements, and it is best to use one rated for at least 15A / 125V, as NEMA 5-15P goes. Besides, users are advised to look for safety marks from Underwriters Laboratories (UL) or the Canadian Standards Association (CSA), which indicate that the device has been certified safe for use. Otherwise, these adapters should be monitored only to improve the distribution of amperes and the prevention of power electrical glitches.
Universal power and splitting systems have been proven to help enhance electrical apparatus connectivity beyond the typical wall outlet. In this way, people can connect multiple devices to an ordinary power-distributing unit or a basic PDU, achieving optimal utility in houses and other commercial spaces. Before purchasing a universal power splitter, one should take into account the total load that will be applied to all devices connected and adjust the connected devices so that the total enlisted current under no circumstances exceeds the rated capacity of most common splitters, which is 10A or 15A depending on the model of the splitter. It is also reasonable that splitters have an internal surge protector or an internal fuse to prevent voltage overload, as it will help increase the durability of the equipment connected to the splitters. Like in any other electrical configuration, the risk of equipment damage or fire should be minimized by compliance with safety standards and procedures.
A: The IEC320 C13 outlet is a constant connector adapted to the plugs of most electronic furniture’s electrical power charging cables. It is usually found on computers, monitors, and servers.
A: Several types of devices, such as computers, LCD monitors, servers, and power supply units, tend to connect using an IEC320 C13 connector, mostly for power.
A: The rated voltage of the IEC320 C13 outlet is normally capped at 250v, so it’s reasonable to use it in several countries.
A: The IEC320 C13 connector can be regarded as a female connector with a socket to link the cables, whereas the IEC320 C14 plug is a male cable fitted into the C13 socket to supply current.
A: Of course, the rated current for the IEC320 C13 connector is 10 A so that it may be used for many electronic peripherals with high energy consumption.
A: A C19 connector is a bigger, higher-capacity connector meant for devices with more power needs, as opposed to the C13, which is smaller and meant for less-powered devices. The maximum current that C19 can carry is 16A.
A: Compatible power cables with an IEC320 C13 socket include cables with an IEC320 C14 plug, 5-15R outlet, and other IEC-type connectors. These vary in length, with the most common being 6 feet, 10 feet, and 1.5 meters, which are mainly used for IEC 320 C13 power connector cables.
A: Right-angled IEC320 C13 connectors are used in confined areas where straight connectors may not be used or are prone to chewing. They allow for a safer and neater fitting of equipment.
A: Detachable cord sets that utilize the IEC320 C13 connector provide modularity, remodeling, and ease of power management of equipment, especially in places with many such pieces, such as data centers and server rooms.
A: Certainly, a splitter power cable can be utilized with a C13 power outlet to share a single power source among many different devices, making power distribution more manageable in areas such as server racks.