Breakout cables are very useful in data distribution in networks today; this is the case because of advances in the modern telecommunication setup. This instructive guide will seek to furnish readers with adequate knowledge about breakout cables, their construction and purpose, and so forth regarding their particulars and applications within a fiber optic system. The different kinds of connectors in use will be explained to the audience, and the role of fiber optics in enhancing communication systems will be highlighted, as well as what has to be factored in when choosing the suitable breakout cable for a given application. In clarifying these aspects, this article provides complete satisfaction to professionals in the industry, network engineers, and anyone interested in the technical details of tasks and solutions for data transmission and communication integration.
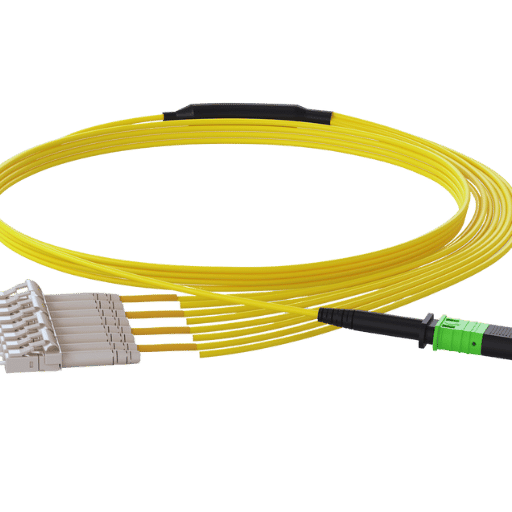
Breakout cables are made up of several separate fiber optic pieces that are enclosed in one outer sheath. Each strand is a bit more independent, allowing for easier installation. Their ends are fitted with connectors for connection to different types of networks o The important properties of the cables are that they can bend and fit into tight spaces and can also survive adverse weather conditions. Therefore, cables are very helpful in data centers, telecommunication networks, and long-range communications, and hence can be said to aid in the effective transmission of data.
Due to their structurally strong and flexible design features, breakout cables have a variety of applications. In data centers, these are used to connect devices to high-density fiber optic patch panels and thus help to streamline data distribution. Breakout cables are employed in telecommunication networks to connect switches and routers, enabling long-distance, high-speed flow of data. In the same way, such cables are also used in enterprise networks for connection between main distribution frames and active equipment as well as for communication purposes that need the bandwidth. When employed, they can find applications for both outdoor and indoor uses, including in industries and at home.
In general, breakout cables can be distinguished by several used parameters like the number of fibers, types of connectors, or specific operating performance. The most common types include:
Data and Performance Specification
These different types of connectors enable the breakup cables to be used in various applications while ensuring effective performance in relation to the demands of the respective network.
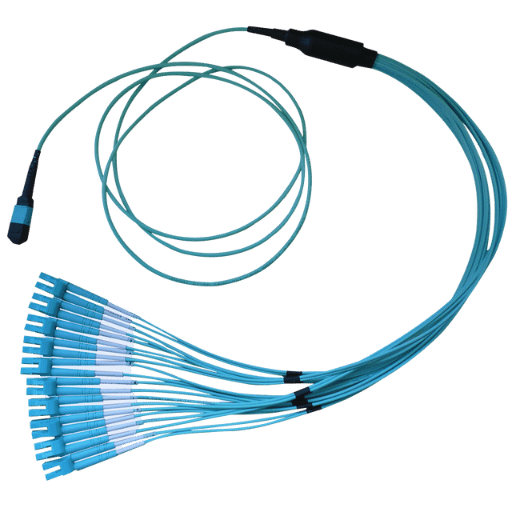
Breakout cables are essentially bundles of fiber strands placed in a single sheath, usually constructed of ruggedized design for better durability. Each fiber is supported by a strength member and can be easily managed as a single connector, being separately connected to ports. The portion of the fiber consists of glass, which is encased in cladding that serves to reflect the light back into the core, thereby optimizing signal transmission efficiency. Also, the materials are used to improve the outer covering so that it is resistant to impact and harsh environment conditions to ensure proper function even in different conditions. This arrangement provides a provision for the present networks without compromising performance reliability.
Breakout cables are made to support a range of plugs so as to maximize functionality, as well as ensure that all compatibility issues with other components of the networks are addressed. The common connector type on the breakout cables are:
Each connector type also has its specific concerns which relate to the compatibility of resolutions, size, coupling system, and performance. The selection of the connector is one of the key aspects in order to achieve maximum performance and efficiency of the breakout cable during networking.
Breakout cables are quite flexible in design in that they can be designed to suit the expectation of different networking arrangements or their performance requirements. The most common configurations are:
Remembering these configurations is important since it aids in determining proper networking solutions currently and in the future as far as bandwidth requirements are concerned. Ensuring proper cord selection leads to efficient operation and minimizes the hardness of cables in the enclosure housing communication equipment or a data center.
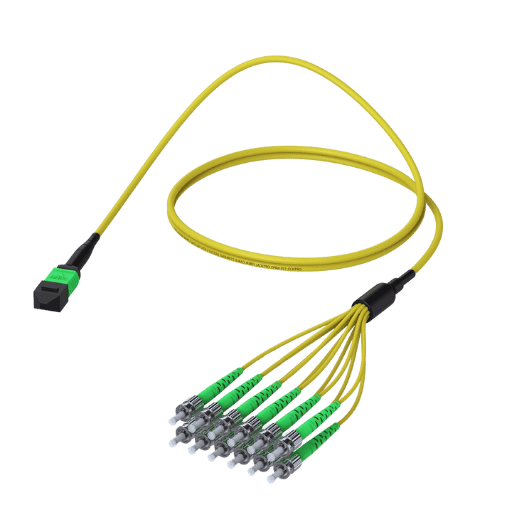

In the case of fiber optic breakout cables, there are a few things that need to be considered.
Properly assessing these factors will ensure that the network operates reliably and optimally.
In assessing the parameters of cable length and speed performance for optical fiber breakout cables, it should be noted that there is also a measure of compromise on signal quality as well as transmission efficiency. The maximal possible length of the cable accounts for one of the factors essentially determining the amount of signal lost and, consequently, the amount of data that can be transmitted in that distance. For multimode fiber, the usual maximum recommended distances for acceptable performance is usually not more than about 300 meters, while for single-mode fibers, distances of over 10 kilometers are common depending on the application and the type of fiber used.
In addition, the respective data rates are dependent upon the type of cable and the connectors, such as for example OM4 multimode fibers, which provide 10Gbps of data for distances of around 400 meters, while single-mode fibers support even faster data (40 or 100 Gbps) for relatively longer distances. As a result, it would appear wise to examine the compatibility of the cable length to the mean expected data rate in the present, and in the years to come, the effectiveness and efficiency of the network operation will be maintained.
While choosing breakout cables for cross-connects it is important to consider the differences that exist between Direct Attach Copper (DAC) cables and Active Optical Cables (AOC), as both have specific areas where they perform well.
In a nutshell, the decision between DAC and AOC is mostly made based on length, factors relating to the environment, and the client’s pockets, and this highlights the importance of comprehensively assessing the particular use case by network designers.
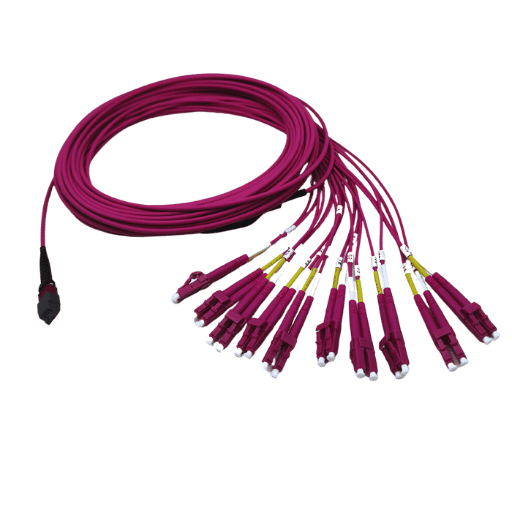

These are some of the key points that need to be followed while preparing for setting up the Ethernet and fiber breakout cables.
Establishing effective connectivity with Cisco and other networking devices involves undertaking some key steps. Before anything else, it is necessary to check if the breakout cables fit in the network interfaces of the device. For Ethernet connections, it should be checked if the cable category is as required and the devices support the respective data rates. For fiber connections, check that the mode of the connection, either single-mode or multi-mode, complies with that of the issued transceivers.
The next aspect to address is the setting up of network settings, which include the IP address allocation and subnet masks, as well as the use of network management software or the device’s command line to turn on the required protocols. Afterwards finally, a number of diagnostic tests on the network are to be executed in order to check the correctness expected of the established connectivity, exploring the reliability of the data transfer and time lag productivity; the availability of the latter can be scrutinized through advanced troubleshooting measures. Preservation of clear and contemporaneous records of these settings will help when dealing with possible problems during the next system configuration and change.
Several performance optimization methods make the most use of the breakout cables to support and enhance data transfer in the system. First and foremost, it is essential to select the right type of cable applicable to the specific requirements of the application and data rate. For example, high-quality Category 6 or Category 6a cables on Ethernet networks have considerably less crosstalk, and bandwidth improves over the traditional Category 5e cables.
In addition to that, proper management of cables may also contribute greatly to performance enhancement. This includes avoiding sharp bends, making optimal cable lengths to avoid cable losses, and doing a proper job at labeling to acutely ease the process of troubleshooting and maintaining the system. In addition, getting active performance management capability can help find obstructions and make needed network modifications in time, leading to normal connection stability and good output. Finally, yet importantly, regular updates on the network devices’ firmware need to be exercised as this performs well in resolving most concern performance issues and enhancing support for breakout cables.
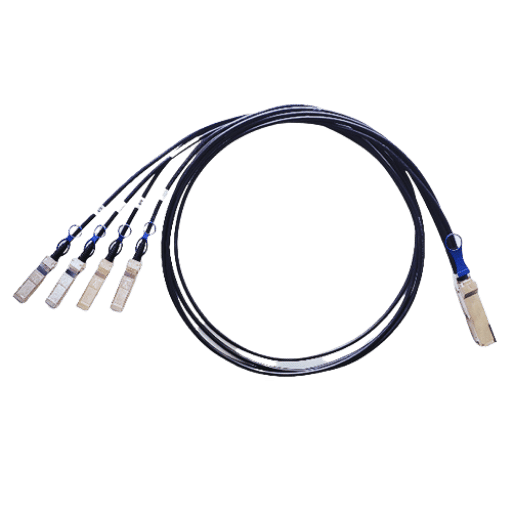

Breakout cables play an integral part in the configuration of networks inside the data centers, particularly due to their enhanced availability and expandability characteristics. They make it possible to connect few servers to one switch port, facilitating traffic distribution efficiently. Such cables support a number of networking structures up to including 10G and 40G connections, while remaining low latency and high bandwidth. Furthermore, breakout cables also assist in preventing excessive cable management that can result in overheating and inefficiency in such tight spaces. Other measures such as using these cables in data centers optimally, by improving maintenance practices such as regular checks and conforming to the cable standards.
In high-speed networks, breakout cables act as manifold resources by data traffic movement across a number of paths from one main port. Targeting 25G, 40G, and 100G Ethernet technologies allows for an increase in bandwidth utilization without adding extra switch ports. Thanks to breakout cables, network designers are able to attach more than one tool, such as a server or storage, towards one switch bare that discounts port consumption toward achieving a better network performance. Moreover, scope dimensions and module usage with respect to the cable materials are also important as they influence the signal quality and time delay which are necessary for efficiency in the modern network undertaking.
In order to maximize the performance of breakout cables in such networks, maintenance and troubleshooting activities should be undertaken on a regular basis. Here are some key tips:
In conclusion, by adopting the above recommendations, it will be possible to prolong the life of breakout cables in particular, as well as the whole system in general, and therefore ensure better performance in high-speed networks.
A: A breakout cable is a type of cable that allows one connector to be split into several connectors, enabling the connection of several devices through one cable. These cables are used mostly in the field of networking and audio to reduce the number of ports needed or to simplify the configuration of many network devices of different speeds.
A: Stereo breakout cable is a type of breakout cable which breaks out the stereo signal into two separate mono signals that are utilized in any audio or video device to control signaling. In situations of multi-media, it is frequently used to attach one channel of a sound mixer or machine.
A: The decision regarding the fiber type depends upon your application requirements that is marketing future application. As an example, single-mode fibers are the best for long transmission while multimode fibers are best suited in shorter transmission spans but with high data rates. All these aspects can be correlated in a way so that they will assist in identifying the fiber type suited for your network.
A: 10g SFP (Small Form-factor Pluggable) and 40g QSFP (Quad Small Form-factor Pluggable) are transceivers utilized in networking. 10g SFP is utilized as a fast serial channel to support transmission rates of up to 10 Gbps, while a 40g QSFP is also utilized in support of transmission rates of up to 40 Gbps, which hence increases the data rates and the port density of networking equipment enclosure.
A: Yes, breakout cables can be used with copper twinax cables. Twinax copper breakout cables can be found mostly in data centers for distance high bandwidth applications and would be 4x10G or 4x25G, etc, for connecting more than one device.
A: Breakout jumper is a device used for joining multiple individual connectors into one. It is helpful and reduces the number of connections as it brings all the connections into one cable, thus helping to manage and arrange wires in complicated configurations.
A: 40g breakout cables divide a single 40G cable into ‘N’ no. For connections of 10G (e.g. 4X10G), whereas 50g breakout cables are the advanced cables that can also be split, but this time to more than 25G connections (4X25G), the option chosen here will depend highly on the data rate requirements as well as the network configuration in place.
A: Adapters in breakout cables are devices which are meant to connect different connectors and ports in ajudging different equipments in a network system. They are helpful in circumstances where the available equipment have different ports or in cases when there is a migration to new equipment.
A: A multicultural breakout can refer to the construction of several standard lower capacity connections from a single high capacity connection to utilize properly divergent from other such lines. This is commonly utilized in data centers and enterprise networks to make the right use of high speed ports and attach different speed enabling network devices.
A: This ‘Breakout’ mode enables one high-speed port to be divided into several low-speed ports so that available ports are optimally utilized and offer flexibility in network recommendations. This use is prevalent in data centers where port persistence is necessary, and network equipment is efficiently utilized.