Electric signals were exchanged in the telecommunications sector for the better part of the 20th century. However, today’s consumers prefer high-speed internet over electric signals. Laser light transmission from one place to another is the most effective technique for effective communication over long distances. Tested and proven across commercial boundaries, fiberglass core braids operate seamlessly over long distances. However, as we opt to use more transmission braids of fiberglass cores, questions of how these communication braids would be spliced together remain unaddressed. As a telecommunications-based nation, operators must be prepared to manufacture, manipulate, and test such braids at an entirely new scale. By creating specific theories for developing new synthetic structures, inserting thermoplastic polymers, and ablating specific connectors to improve efficiency, engineers must make rapid changes in their designs, techniques, and processes and prepare themselves for what is shaping to be a whole new game. Throughout this blog, all these topics are elaborated, in-depth details are provided, and information that emphasizes their importance is presented.
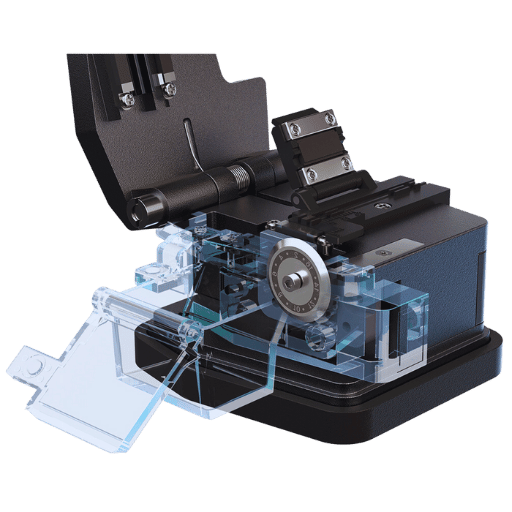
Cleaving of fiber optic cables is achieved by a fiber optic cleaver, a tool that has been manufactured to cut fiber at a radius angle high enough not to damage the ends of the fiber. It remains one of the most essential tools employed during fiber optic preparation processes such as fusion splicing. This process includes placing the fiber into the cleaver, dividing the glass fiber with a sharpened blade, and pulling the fiber in a specific amount to cut it. This guarantees that the fiber end surface is perpendicular to the axis of the fiber, which minimizes losses and maximizes the transmission of signals in optical networks. Other cleavers have various features, such as adjustable angles and blade life indicators for different splicing needs and fibers.
In order to guarantee quality and efficiency of fiber optic splicing procedures, fiber optic cleavers are imperative. As per the present-day agreed sources, the above steps are carried out precisely during the cleaving procedure: clamping the fiber, scoring the surface, and making a precise break. This break is significant since it completes the end face of the fiber, and it is this face that, during splicing, determines the insertion loss and return loss. Automation functionality minimizes manual intervention and, thus, reduces the reliance on human manipulation, resulting in improved accuracy and repeatability of high-end fiber cleavers. Approximately 50,000 single cleaves are expected to be done before blade or wheel replacement, which adheres to the principles of technical advancement at a lesser expense. Other newer models could include automatic handling of fiber scraps and fiber optic rotary splicers, which help increase the throughput while maintaining the quality of the construction in fiber optic networks.
The term cleaving’ is synonymous with the phrases ‘to fabricate’ or ‘to divide’ and, therefore, would require a precise cutting tool, and the cleaving blade performs this function. In the context of fiber cleaving, the blade constitutes a strong component. High-quality fiber optic connections depend on the cut’s accuracy and performance, which is largely determined by the cutting tool that performs that task. In various cleaving stages, high stress is transferred onto the impact point, bringing about substantial losses on insertion and back reflection, which results in energy loss on the optic signal. Precise fiber cutting enables automatic micro-adjustments, sharpness, and later angles of the cut’s position to be maintained within specified parameters by advanced cutting systems. One of the major bolts of the downfall and disgrace of optical networks has been attacks on fibers, but precise fiber cutting and cleaving make avalanches much less frequent, thereby promoting longer peripheral life. Such a cutting system will directly increase the optical yield and reduce fiber downgrade cuts and maintenance expenses.
The field of fiber optics must be treated with a lot of precision because it ensures better connections and wide network dependability. Numerous sources available in the market point out that this precision of assembly affects the proper positioning of fiber cores, which is critical for light to pass through with the lowest possible attenuation. Cleaving with high precision accommodates smooth fiber ends, which, together with low profile connectors, decreases the insertion and back reflection losses, hence protecting the data. Furthermore, high precision minimizes the chances of any mechanical failures and increases the lifespan of components in a network. Therefore, precision in fiber optics leads to extensive restoration costs and high operating efficacy of networks, lowering requirements for restoration, as repeatedly emphasized by most renowned sources of fiber optics.
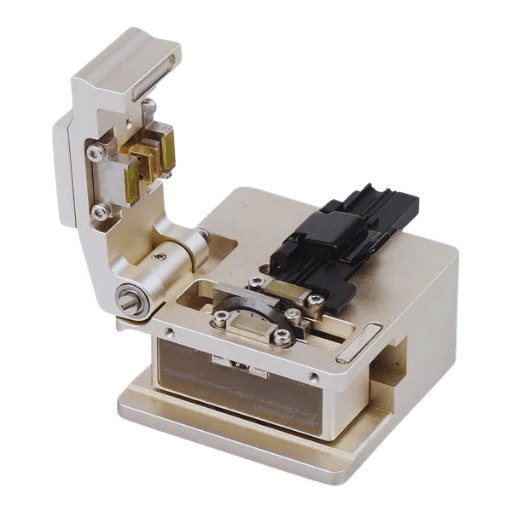
This will allow users to improve the quality and reliability of their fiber optic connection, resulting in better network utilization.
In cleaving fiber, I have realized that some common errors stem from a lack of preparation and positioning. To begin with, the cleave quality might be compromised if the fiber is stripped the wrong way or if the boundary glass has impurities on it. I always use an efficient stripping tool to eliminate all the imperfections. Second, incorrect placement in the cleaver is one of the most common problems; The fiber has to be straight and under the right amount of tension for an excellent cleaving angle. Finally, I also make it a point to check whether the used cleaver blade is sharp enough, as the tip of any particular edge may not be sufficient to produce qualified cleave angles. Focusing on these finer points enables me to get the best connections.
There are practices I follow to keep my fiber optic cleaver in excellent condition. First, I clean the cleaver after each use, ensuring no fiber bits are left to avoid any subsequent build-up that can block functionality. Second, I make it a habit to examine the cleaving blade and look for any signs of wear. I recognize that a dull blade is an enemy to executing an accurate and smooth cleave. Similarly, I also check the calibration of the cleaver according to the manufacturer’s recommendations at regular intervals. Also, dust and corrosion are one of the materials that can easily damage a cleaver; this is why I keep the cleaver safely tucked in a casing when I am not in use, it also extends its life span. All these maintenance tips I have elaborated on allow me to say the cleaver is precise and effective confidently.
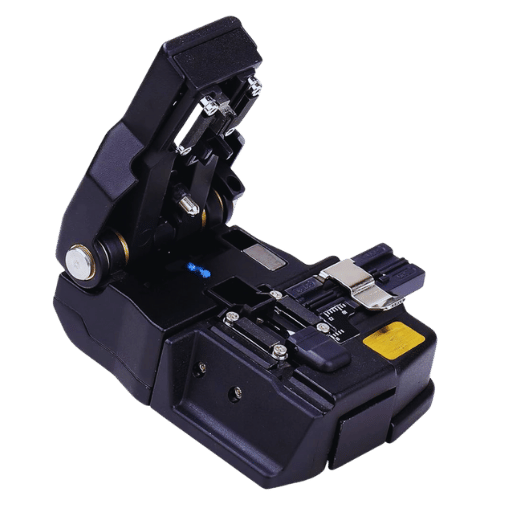

In order to achieve accurate results, a high-precision fiber blade is expected to have several critical blade properties. The first property is the material of the blade, which should be of good quality and strong enough for many uses, like tungsten carbide or diamond. Another critical aspect is the blade’s sharpness; having a sharpened edge will ensure that all the connections, especially the fiber-optic ones, will be done with various connections that require clean cuts. In addition, the blade’s edge should be angled at a constant degree to facilitate cutting fibers of different sizes, especially those with a few micrometers and a gap of a few microns in size. Furthermore, the blade tension and blade position must have adjustable settings. These characteristics combine to make a fiber cutter more effective and durable as they aid in making high-precision cuts.
Cleaving is essential during the preparation of fiber optics since this is the stage when the fiber is carefully scored and snapped to obtain a clean and even end face that is ready for splicing or termination. This process is done by a highly accurate fiber cleaver that holds the fiber in place and applies some pressure to the glass to score it, and then a slight tension is applied to snap it off. The intention is to form a 90-degree cut at the end of the fiber so that there will be a minimum reflection of the light signal, which is critical for signal transmission in most cases, especially single-mode fibers. The accuracy of the cleaving process directly affects the effectiveness of the fiber optic joints, which implement suitable quality devices and skills necessary, especially when interfacing with laser systems.
Selecting a clamp qualifies as one of the critical elements in setting up the fiber optic structure. Because the cleaving process is prone to misalignments and instability, the proper clamp must be selected early. To know the appropriate clamp, consider the types and diameters of the fibers you are using. The clamp should fit these parameters to avoid damage while providing a firm grip on the cladding. Also, consider how much your clamper and turning equipment can work together, as clamping is the initial stage of effective functioning. Start with clamps made of solid and nonmarring fiber lines, which will avoid making a mud pie out of the fiber. After that, adjustable clamps can provide the flexibility needed to hold a range of fiber across a project, along with features such as tensioning used throughout the entire project cycle. Always remember that selecting a suitable clamp when cleaving the fiber optic ultimately improves the quality and intensity of the signal.
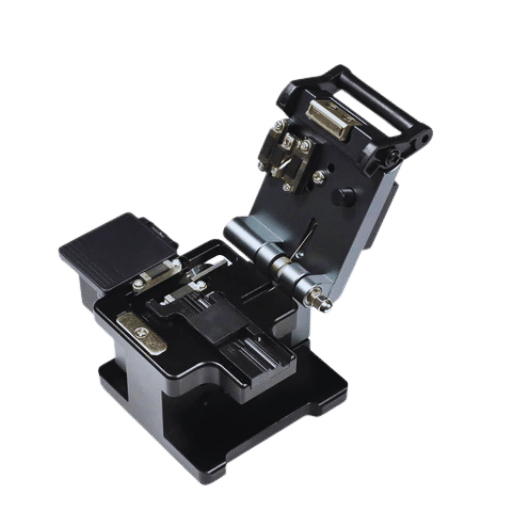

When evaluating models of fiber cleaver, it is essential to consider features that affect performance and specifications, including those made for high-precision fiber cleaver tasks. Always check the automatic blade rotation feature on some models, as it increases the blade’s lifespan and enables adequate cleaving quality. Evaluate how easy it is to change the blades and how much it costs. Furthermore, the angle of cleaving in the fiber optics functions is critical, so seek models designed to cut precisely at 90 degrees to avoid signal degradation. Check if the regular cleaver covers the range of fiber diameters you use to have flexibility in your projects. Ease of use, such as ease of adjustment and a position for interaction with the user, is also essential, especially in mass production processes. Some models have integrated collection bins for waste fibers to improve safety and a clean work environment. Given this set of characteristics, you can select a cleaver that best suits your operations and budget and effectively promotes your fiber optic installation operations.
When choosing a fiber optic cleaver, several criteria should be considered to determine whether it suits your specific needs, such as compatibility with fusion splicer fiber systems. These include:
According to their reputation and technological-based innovativeness, the brands that managed to attain a competitive advantage in the industry include Fujikura, 3M, and Corning. Amongst its customers, Fujikura is best regarded for its state-of-the-art cleaving tools and splicing equipment, which are trustworthy and accurate. Corning has more than thirty years of experience developing and manufacturing high-quality cables. As an innovator of fiber optics, the company is fully committed to research and development to improve network performance and toughness. 3M is well-known for providing a wide array of fiber optic products while placing great attention on simplification of use together with new developments oriented towards the fast-changing requirements of the connectivity infrastructure. These brands complement each other in some ways by providing a wide range of products and simultaneously focusing on efficiency, thereby considerably improving the quality and reliability of fiber optic systems.
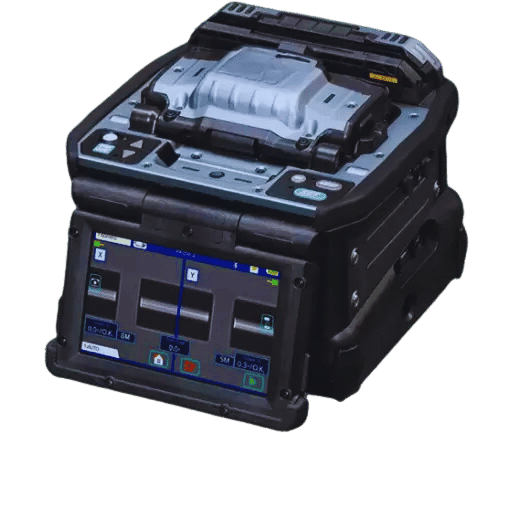

In fiber optics, fusion splicing is one of the most important, as it significantly influences the integrity and performance of the network. It comprises the end-to-end contact of two optical fibers by welding them using an electric arc, which results in low signal loss and back reflection. It is more useful than mechanical splicing in situations where environmental conditions may change because it allows for a continuous fiber route. The major contribution to the efficiency of fusion splicing lies in its low insertion and high return losses, making it most suitable for backbone network systems. In addition, technological development has also helped make the equipment more straightforward and more versatile, ideal for different types of fibers, and improving the quality of the splice, reflected in the performance and the life of the network.
Cleaving is a critical preparatory process during the fusion splicing task and directly affects the quality and efficiency of the splice. A correct cleave alleviates the splice loss as it eliminates the roughness on the edges of the two fibers and also makes them perpendicular to each other. This accuracy level also helps achieve the required alignment at the splicing stage with minimal physical contact interference in the light path. As established in the literature, if the cleave is poorly executed, some distortion and surface irregularities would be introduced, increasing the splice loss and signal degradation. Using specialized cleaving tools that provide variable tension and angle settings increases the cleave effectiveness, leading to improved network performance and reduced maintenance needs.
Combining fuse splice with fiber cleavers is a well-organized method aiming to get the best splicing results. A fiber cleaver does what needs to be done for a splice to be effective and of high quality, which gets to the aspect of effective fusion, enabling automatic devices to be integrated with fusion splicers. When automated, the systems can manage the cleaving and splicing procedures simultaneously, eliminating possibilities of alignment faults and insertion loss. Built-in communication functions in today’s merging splicing apparatus perform flawlessly with the corresponding fiber-cutting devices, increasing the overall ease, speed, and precision of the processes involved. This integration reduces errors from human interaction and speeds up the workflow, which helps improve the performance of a network and reduces downtimes.
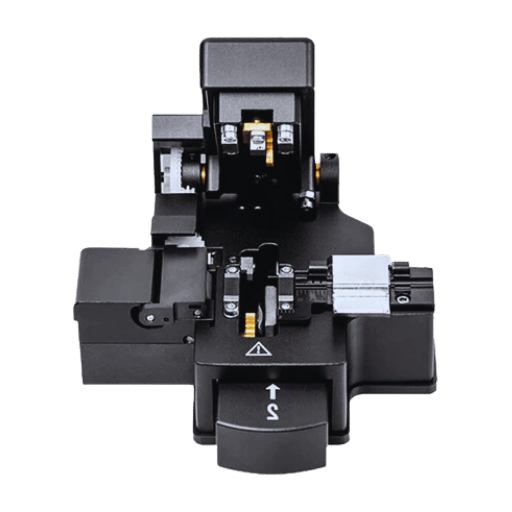

A: An optical fiber cleaver is a tool for cleaving an optical fiber correctly and accurately. It is critical for preparing the mating surfaces of spliced or terminated optical fibers, as it ensures that the end face is flat and smooth, thus avoiding excessive signal loss and enhancing the quality of the connection.
A: Comparing works on a standard fiber cutter and the Jonard Tools FC-500 precision cleavers, the FC-500 demonstrates better consistency and accuracy than normal cutting tools. It is essential because low-loss cleave angles (particularly in the optical networks splices and terminations) of up to 0.5° angle or less are standard in the offs.
A: The most common fiber types, which have a 250-micron diameter (bare fiber) and a 900-micron diameter (coated fiber), are single-mode and multi-mode—these can all be cut by fiber optic cleavers. Some high-end models add the capacity to cleave FTTH ribbon fibers.
A: It depends on how much it is used, but a blade should be replaced after performing between one thousand to three thousand cleaves. Many cleavers from companies such as Sumitomo or Jonard have simple blade replacements for easier cleavage maintenance to perform precisely.
A: For cleaving in the field, a compact lightweight cleaver has strong fiber clamping, ease of blade change, and the ability to leaf both 250µm and 900µm fibers. Some even come with an integrated scrap collector and a case, which are fit for fiber technicians who operate in different places.
A: Yes, various fiber optic cleavers are meant to complement the fusion splicer fiber systems in splicing, which is efficient yet. These implements make accurate cuts, which are necessary for successful fusion splicing. There are even some fusion splicers that have a cleaver built into the system.
A: To achieve a clean and precise cleave, ensure that you perform the following tasks: 1) Clean the fiber strand completely, 2) Remove the coating, being careful not to cut the fiber, 3) Lock the fiber in place inside the cleaver’s fiber holder, 4) Position the fiber with the right orientation, 5) Maintain a uniform force during the and cleaving, and lastly, 6) Check the cleaved edge under a microscope or fiber scope to ensure it’s up to standard.
A: While fiber optic cleavers are usually versatile enough to splice different types of connectors, some have been designed for very specific ones. For example, some cleavers are designed to be used specifically with mechanical splice connectors, or some even have specific angle cleavers for certain types of connectors.