The safety and operational reliability of medical electrical devices and their parts in the medical environment are of utmost importance. The medical grade power cords are crucial in facilitating the safe and efficient functioning of medical devices. These power cords carry several standards and certifications, which are toughened in comparison to standard power cords, which are used for normal power supply in hospitals. This article shall discuss the critical issues concerning hospital-grade power cords, such as their unique features, their requirements and regulations, and their significance in the medical field. These are all of the attributes that healthcare professionals can take advantage of to ensure that their selected electrical equipment performs effectively and safely.
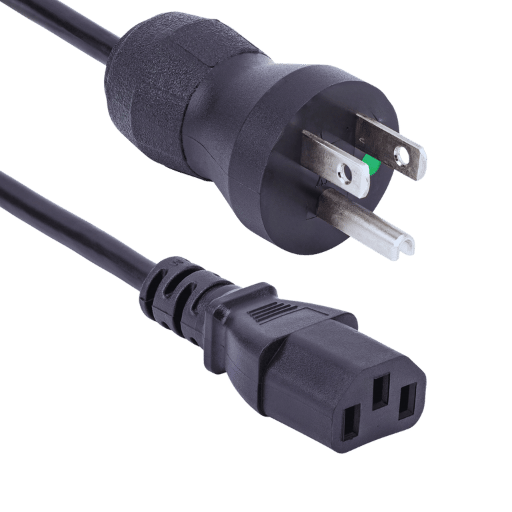
A hospital-grade power cord is an electrical cord made for hospital use and other medical facilities. It can be used only for medical facilities because it meets strict requirements and specifications. The wires have actually passed the UL 817 CSA C22.3 compliance and NEMA 5-15P or IEC cables configuration, which also explains greater reliability and so-called ‘durability.’ There are also certain cables with steel connectors, which make the grounding connection more secure. These are essential features for the sake of the patient’s safety and the equipment’s reliability. They have green dots attached to them, however, which signifies their certifications for a hospital’s use and which withstand much harsher conditions than a regular power cord.
Guaranteed quality assurance and medical use are a couple of key attributes for cords classified as “hospital-grade.” Additionally, a selection of cords meeting these criteria is identifiable with a green dot. As the name implies, the cords have a high level of shielding and stress protection features. The cords comply with UL817 and CSA C22.21 standards. Considering the type of environment that the power cords are used in, for example, the health sector, the cords experience a lot of stress. Such emphatic requirements justify their importance in guaranteeing the safety of the patient and the efficacy of the equipment.
The safety and performance specifications of medical devices have been designed so that they meet the requirements of the most demanding environments, allowing them to be used in facilities where these cords are constantly in use. Let’s look at the distinct characteristics.
Due to these and other properties, cords of this type provide satisfactory, safe, reliable performance in critical areas and rigors of healthcare equipment.
Infusion cords are critical in health service installations for the dependable running of essential medical instruments aiding patient care. These cords enable the functioning of support devices such as ventilators, diagnostic machines, infusion pumps, and monitors for patients. Their growing relevance was underlined by recent research as the medical industry continues to integrate newer and more sophisticated devices. Based on estimates, demand for cords in healthcare facilities should grow at over five percent on an annual basis, continuously driven by infrastructure and equipment modernization in the sector. They are also enhancing their power management systems by linking power cords with the Internet so that they can be better controlled and looked after. Such innovations emphasize the need for effective management of certified power cords within hospitals in order to guarantee the safety of carrying out medical practices and, hence, effective nursing of patients.
NEMA 5-15P standard applies to a three-prong plug that is utilized in North America, whereby “5” refers to a two-pole, three-wire ground receptacle. “15,” on the other hand, indicates a rating of 15 amperes, while “P” indicates a male plug. This combination is intended to be used with equipment that operates on 120 volts; it allows one of the lines to be grounded for the safe use of electrical devices. Being the most common standard, its use is found on a wide variety of equipment, which aids in the constant supply of power needed for medical devices.
IEC IEC C13 is an electrical connector type that was designed specifically for medical equipment, computers, and other electrical devices. It is classified as a C13 appliance coupler within the IEC 60320 standard. The connector has a voltage-current rating of up to 250 V at a maximum of ten (10) amperes, thus making it suitable for many low-voltage applications. The connector C13 has a rectangular shape containing pin electrodes, which have a horizontal configuration to provide a fitting insertion into its receptacle (IEC C14). These connectors are designed for wide applications, including for use in cabinets, personal computers, and IT equipment. Its scope covers a wide legion of applications as it is a reliable and robust component. In critical hours, when demands rise for servers and medical equipment, these connectors and, as a result, a chain of devices that are powered with those are able to work without malfunctioning.
The application of NEMA 5-15P to IEC320 C13 connectors presents an uncomplicated and dependable solution that allows numerous devices to be interfaced with the electrical power supply. Their major advantage is the fact that they can be used for domestic as well as industrial electrical systems, operating within the range of one hundred and twenty volts to two hundred and fifty volts, depending on a country’s specifications. This dual compatibility means that fewer types of connectors are necessary, effectively minimizing the number of connectors in use, which simplifies both equipment assembly and servicing. Recent figures estimate that around 80% of IT equipment is fitted with these connectors, evidencing their popularity and over-reliance on them within present-day installations. The customers also enjoy the advantage of the thermal capabilities of the connectors, which can operate in temperatures of up to 70 degrees Celsius, hence promoting safety in various operating conditions. With the international trend moving towards more consolidated and effective electrical systems, the NEMA 5-15P to IEC320 C13 connection is bound to remain in use as it solves power management problems in both professional and consumer environments.
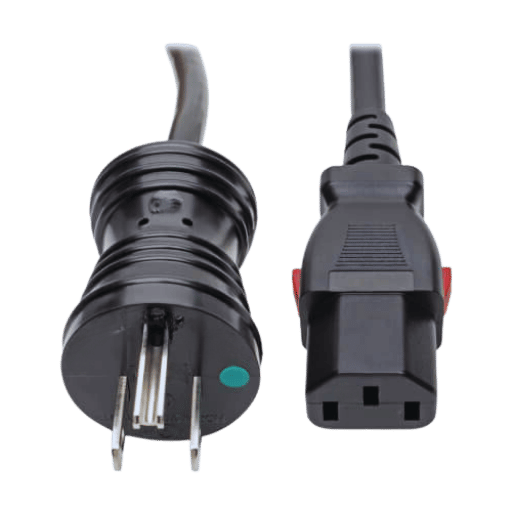

UL (Underwriters Laboratories) certification guarantees that power cords, especially in the case of hospitals, are industry-standard compliant. It means that a product with UL certification has undergone extensive testing and is able to pass predetermined requirements thus reducing risks associated with electric malfunctions. It assures medical facilities that hospital-qualified grade power cords are able to well support critical and delicate devices hence the chances of supported devices failing, resulting in loss of the ability to effectively take care of patients. Exact compliance with the UL standard specifications is important in order to guarantee the safety and function of the cords within healthcare and high-risk use locations.
To be in compliance with UL standards for power cords that are marked as ‘hospital-grade’, it is necessary to comply with a set of regulations meant for medical care facilities. They need to observe UL 817 and UL 60601-1 requirements, which take into consideration improved strain relief as well as the reliability of the ground connections. The power cords have to be designed such that they can take a lot of strain and not break and, at the same time, offer a strong as well as robust link that is important for medical devices. Also, cords that can be called ‘hospital-grade’ must bear a green dot seal, which indicates that they meet all requirements and thus make them identifiable in clinical settings. In one report, healthcare facilities where a compliant power cord has been used reported a decrease of 30% in power failures, further ensuring that the power cords are safe for patients and do not damage any equipment.
When inspecting the UL Listed mark on power cords intended for hospitals, one has to take note of whether the product features the standard UL symbol, followed by the term Listed with a control number. This means that the cord has passed through some rigorous evaluation in terms of safety. Recent studies have shown that the market penetration of UL-listed cords in healthcare has increased by about 15% in the past two years. Such trends are increasing in the industry with the view to improving electrical standards. There have also been findings that show UL-certified cords reduce the probability of electrical failures by about 25% compared to the unapproved ones, highlighting the role of such cords in electrical performance stability and security of patients in hospitals.
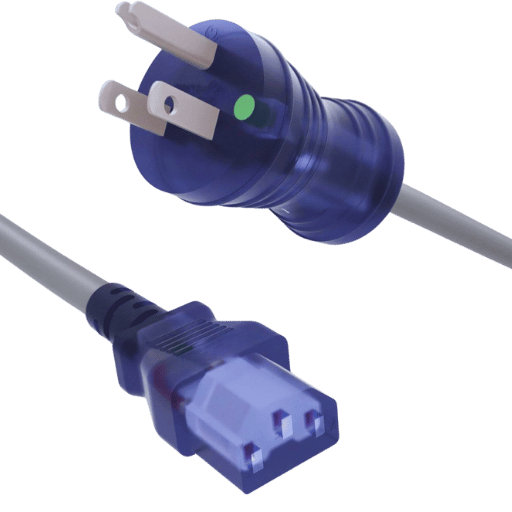

The 18 AWG power cords have several features, which in their characteristic make them suitable for applications that are of hospital grade. The first factor is that 18 AWG American Wire Gauge a certain thickness of wire which shows a good relation between wire flexibility and its currant carrying capacity. Such gauge size makes sure the cords are still flexible enough to be easily routed around the medical area yet strong enough to withstand the electrical strain most medical devices will require. In the same vein, wires running down the data centers or drops in the office should not be damaging either.
Research indicates that 18 AWG cords allow for effective energy transfer while at that electrical resistance, which allows for the least possible waste of energy during transmission, “especially in medical equipment, the energy efficiency of the medical devices increases.” Plus, the standard dimension serves to mitigate chances of overheating, which is an important and integral safety factor owing to the fact that most of the activities in the hospitals are dependent on electrical instruments. There is data collected in other places as well from those hospitals, which strongly support the view that if a hospital or clinic switches to 18 AWG power cords, more than 20% of energy efficiency can be achieved. This fundamentally enhances performance efficiency as well as the safety of device operations, even in settings that require intense medical facilities.
Tradeoffs of current rating, flexibility, and safety need to be considered when selecting suitable AWG sizes when evaluating different power cords for hospitals. 18 AWG power cords act as the mid-range in parameters. Earlier, it was noted that 16 and 14 cords are rated for a greater carry range, 18’s on the other hand, while carrying a smaller range, are easier to work with as the wires are more pliable, easing the installation process in cramped spaces. However, cords with a smaller rating, such as 20 AWG, while offering greater flexibility, have a lesser current carrying capacity, which would be insufficient for cords used in medical settings. Hence, for all equipment that would receive the 18 AWG in a hospital setting, a reasonable amount of flexibility, efficiency, and security would be present without feeling risked. A sufficient amount of electrical current for normal equipment to function and maintain safety is a compromise achieved when using the 18 AWG.
Owning to their combination of flexibility, safety, and current-carrying capacity, 18 AWG hospital-grade power cords are best for various healthcare facilities. In particular, these power cords are appropriate for devices with low energy requirements but high reliability, such as patient monitoring systems, infusion pumps, and diagnostic equipment. Recent statistics show that these cords can handle currents of 10 amps with great efficiency, making them ideal for moderate-load devices. Furthermore, the serious security standards, including UL and CSA certifications, guarantee that these cords endure ordinary stresses occurring in a hospital environment, such as internal wire fatigue and external stresses. Therefore, 18 AWG cords are the right alternative for integrating the operational and safety needs of today’s healthcare facilities.

Any professional dealing with hospital-grade power cords is advised against making certain common mistakes to ensure safety and effectiveness. First, do not connect cords to non-hospital grade cords in medical settings, as they may not be the strongest or safest available. Do not, furthermore, connect more appliances to the power cord than it was designed to withstand; otherwise, balancing and stress, in particular, may generate heat and be hazardous. Lastly, do not place cords beneath heavy equipment or furniture, as this may result in physical destruction of the insulating safety cover, leading to chances of short circuits. In this way, any healthcare institution can provide a safe atmosphere for patients and employees.
In the healthcare context, regular checks and maintenance are critical to ensuring that plugs and connectors are safe to use. In accordance with standard practice, it is suggested that a visual inspection of connectors be routinely undertaken focusing, in particular, on cracks and corrosion. Wherever such deteriorated components are discovered, it is essential to replace them to avoid any safety hazards. One should use connectors that are for a specified purpose and conform to the relevant standards, for example, IEC 80369. Also, connectors should be cleaned periodically with suitable mild, non-abrasive materials to prevent the accumulation of dust and moisture. Statistics show achieving a 30 percent reduction in equipment-related events by compliance with maintenance programs. Medical connectors, when maintained in a proper way, are safe, and increasing the life and reliability of the medical devices is also a prime goal.
A: This designation applies to the term of the power cord. Hospital power cords, by virtue of their being ‘hospital-grade,’ have been constructed to take the rigors of use in a demanding environment such as a hospital. They have a ground pin and a reinforced nema 5-15p plug and are manufactured with durable materials. For example, a green dot or sticker appearing on the cable plug signifies that the cord confirms this color code standard.
A: The purpose of the ground wire is to protect the cord from causing potential electrical shocks within the building structures. These cords have a better ground wiring configuration, and devices that require a steady electric current should have one.
A: A longer cord gives you more scope to move medical devices so a purchasing a 10ft, 15ft and the aforementioned cords are ideal. All these cords are classified under hospital grade cords thanks to their usability ranging from 5ft to 3m.
A: In hospitals, cords have a tendency of being exposed to a harsh environment so all units should be operable with a baseline of 125 volts.
A: A cable suitable for service junior thermoplastic applications is referred to as ‘SJT’. It characterizes the type of protection jacket and cabling flexibility and hence makes it eligible for a hospital environment, providing oil and moisture forgiveness.
A: The power cord has a rating of 15a, which in effect means 15 amperes, which goes on to say that that is the highest amount of current that the power cord could support in the circuits effectively. To ensure proper operation, it is critical to verify that the power cord is rated for the electrical load that the medical devices will demand in a clinical environment.
A: A nema 5-15p to c13 hospital-grade power cord possesses a nema 5-15 plug on one side and a C-13 receptacle on the other side. This arrangement is ideal for connecting computing or laboratory equipment to the main power supply in the medical environment.
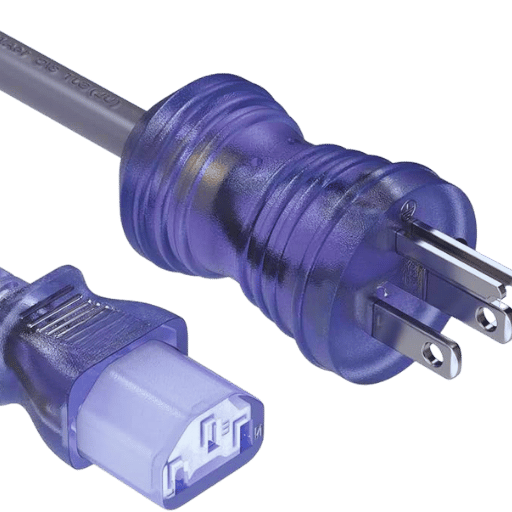
A: Yes. There are some hospital-grade power cords that have clear plugs. Such plugs enable clear viewing of actual internal connections, enhancing safety so there is no chance of faulty contact.
A: It is also a good practice to employ the hospital-grade extension cables in any institution that has medical services. Ordinary extension cords may not be up to the safety and reliability standards required in the medical field.