The importance of keystone jacks in network infrastructure is something that must not be underestimated. Primarily used for data communication, they are modular connectors that are capable of transmitting network communication between various devices. Keystone jacks allow for effective connectivity within structured cabling systems that can range from home offices to large commercial venues. This article discusses the nature of keystone jacks, their types, purposes, and their features within the construction and maintenance of a solid network infrastructure. Knowing the applications and technical details of keystone jacks, specialists are able to enhance the reliability and performance of the network, improving its fault tolerance and continuity of operation at all nodes of the network.
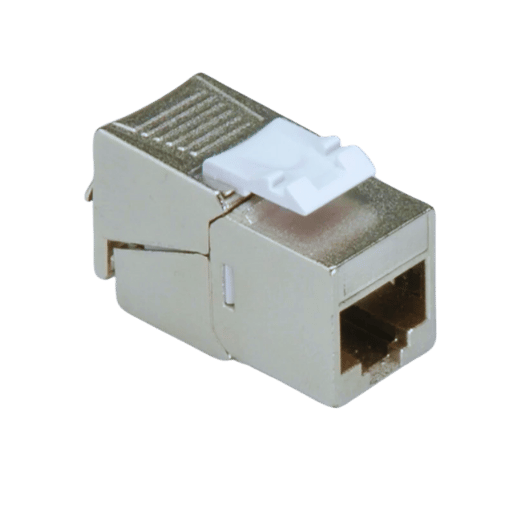

Keystone jack is a module mainly used within telecommunications and data networks. It goes into a keystone wall plate or patch panel and makes connections of a large number of cables to many network devices possible. They are also known as keystone jacks and assist in the transmission of a network data signal through standardized connectors, which are often Category 5, 6, or 6a cables. Their construction is modular, so they can be installed and maintained easily. Hence, they play an essential role in structured cabling systems.
Keystone jack is a device designed to interface with various devices through its modular ports. It is able to convert and transmit data signals and create bridges among the devices. It’s perfectly able. The main characteristics of a typical keystone jack are the housing unit, the IDC (Insulation Displacement Connector) terminals and the front-port connector. A wire’s insulation forms an airtight seal and doesn’t require solder. Because of this, the IDC terminals are vital in locking cables into place more securely. This affords an effective electrical connection for the transmission of data across.
Keystone jacks have 3 networking outlets, which correspond to the following: Cat 5e, Cat 6, and Cat 6a, that are standardized according to their intended use. Each of them has different capabilities in terms of data transfer rate performance and the characteristics of bandwidth; Cat 6a is among the newest and offers a 10 Gbps data rate with 500 MHz frequency. Moreover, they can have a covering or be shieldless, which determines their level of protection against electromagnetic interference in areas that contain a lot of electronic noise. This information will help network specialists find the exactly suitable keystone jack for their specific connection, which improves the overall performance and dependability of the networks.
The manipulation of the cable becomes significant in integration with the keystone as it determines the means and the mode of provision of data communication. The cable, together with a compatible keystone jack, guarantees better connections and less signal breakage. In relation to the respective keystone jack, the cables Cat 5e, Cat 6, and Cat 6a are frequently used to enhance the connectivity of the corresponding keystone jack, each having different data rates and bandwidth. The correct procedures for connection establishment and cable solutions must be adhered to in order to protect the connectors from excess crosstalk and electromagnetic inductive impacts. Carefully assembled cables and their correct placement allow you to increase the performance and work reliability of a network system.
Considering the internet always remains on, it is easy to presume that there exists a seamless plugin of communication tools for data transfer in an infrastructure that is separated from the public, avoiding any downtime. This is enabled by different information outlets, which encompass keystone jacks and patches, which in turn are able to answer the operational needs by catering to VoIP services, high-speed internet, and reliable data center cabling.
Going forward, it would be interesting to explore how data closet along with jacks are able to meet the demands of high traffic whilst maintaining bandwidth in a reliable manner. There is always a requirement of sending up to virtualisation of cloud computing of 10 Gbps and this is achievable through using cat 6a cable or jacks.
In addition to the above, IoT-enabled devices always face the issue of getting plugged in as sheathed cables are used along with the jacks, so this integrates multiple meshed building systems of lighting, heating, and hygienic properties. Thus, it can be proven that there is always a necessity for networking tweaks such as jacks and cables to be adjusted in order to meet the recent focus areas of a business, which is the improvement of speed in the network with high security.

Preparation
Cable Stripping
Wire Arrangement
Placement in Keystone Jack
Punch-Down Execution
Verification
Testing
Proper service and maintenance of the tools should guarantee the continuous and efficient use of the punch-down tools. To make it possible, you must end up cleaning the tool in question after every post use in order to eliminate any possible particles or residue left on the post at the end of the task. Checking is significant as well; check for dull blades or loosened parts at regular intervals and replace parts where necessary. Storage is important- place the tool in a clean and dry place to guard against rusting and corrosion. Proper care of your punch-down tools will not only increase their usability but guarantee the quality and accuracy of your punch-down network installations.
Cat5e and Cat6 keystone jacks, both belonging to the family of network cabling, include distinct characteristics that determine their use and performance. Their structural characteristics and key differences are discussed below:
Bandwidth and frequency:
Cable Structure:
Performance Standards:
Physical Design:
Cost considerations:
These differences are important to understand when making a selection for keystone jacks for deployments in the networks as this will affect the current efficiency as well as the future growth potential of the same network system.
Cat6 keystone jacks have become more popular because of their capacity to support data transmission over significantly longer distances with high bandwidth signals. They are critical components of a network system cable due to their unique ability to provide a permanent link to hardware that can connect multiple devices into one network. Such encrypted devices without point interference would now have been ideal in situations where high interference is expected, considering these devices could connect to a high-bandwidth network. Cat 5e cables can connect CAT 6 jacks to devices, such as routers. However, be sure that upgrading to this faster technology while still using the same devices will not create any future issues and will not become obsolete. The conclusion one could reach about why professional data-jack cable networking jacks prefer this specific model.
Ethernet keystone jacks are essential, as they enable the interconnection between cables and devices in networking. They are also useful for the installation and upgrading of network infrastructure thereby ensuring that data is effectively transmitted with slight or no loss of signals. Their universal design makes them compatible with multiple cabling systems while ensuring that the network functions the same in different settings.
Optimal performance and reliability of network infrastructures will only be achieved if one pays attention to the numerous technical and functional parameters.
Network professionals can carefully evaluate these hosting requirements and choose among the most optimal cables and jacks ensuring the users of optimal and smooth transfer of information in their network.
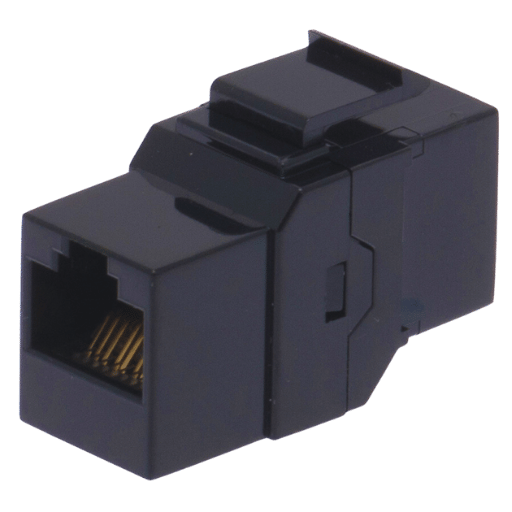

A patch panel helps to reduce the complexity of the network by enabling centralized management of connections, hence improving the organization and identification of network paths. It makes it possible for reconfiguration to be flexible and scalable without the need to directly interfere with the primary cabling system, thus preventing undue stress on the cables. Patch panels make it easier for troubleshooting and maintenance to be carried out with the use of designated access points to specific portions of the networks, and they also minimize clutter at the connection points to help maintain signal integrity.
Completing the installation of keystone jacks and punch-down patch panels is an important step in improving the efficiency of cabling systems. As an extension of jacks, filled with keystone inserts and their jacks’ function, keystone jacks allow the formation of a more robust and adaptable linking framework. The reason for this is the possibility to tailor the network according to every organization’s special needs, like the speed of data transmission or the kinds of cables used.
There can be a rush to use patch panels without understanding the bespoke cutter configurations and cables like cat5e/cat6/cat6a. When in a rush to complete keystone jack termination, the embedding of the cable can be disorienting. Insertion Loss, Return loss, and cross-talk levels must also be measured. Substandard performance during joiner installation and subsequent testing of the installed jumper would place their issuance zones in rela tively bulged sections defined wholly by ANSI/TIA-568.
Further elaborating on the details of keystone integration, the number of insertion and removal cycles is mentioned, the quality of the jack (750 cycles or so), which is above the average, along with the industry standard for terminations. One key factor assisting in achieving this outcome is ensuring that all cables are properly terminated into the keystone jack, as this reduces return loss across the network. The astuteness in the technical procedures results in well-structured, reliable, and robust de facto standards of network subsystems.
Maintaining proper cable organization is necessary for an efficient and effective network topology.
In observing the given best practices, improvement of network reliability is enhanced and the hassle associated with being able to upgrade or repair is simplified.
A: A Keystone Jack is ideal to install a variety of low-voltage electrical connectors into the keystone wall panel or patch panel, since they are all the same shape or size. They are usually found in Ethernet cable systems, especially those that utilize RJ45 connectors because they are needed to make those connections work.
A: RJ45 Keystone Jack is specifically encapsulated to accommodate Ethernet cables and is also widely used for connectors in keystone which are part of network system infrastructure. Moreover, it enables the interfacing of the Ethernet cabling marked with the 8P8C scheme of up to Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a and more.
A: The punch-down tool is used to attach cables along T568A and T568B color codes with its marked applications, also called punch-down plugs. To attach IDC properly on the keystone jack, wires are set in its slots using punch down the tool.
A: Gold plated RJ45 contacts have enhanced corrosion resistance as well as electrical conductivity, thereby ensuring dependable transference of data across the network and increasing the lifespan of the connection. One great advantage of this is in expanding networking environments where ethernet cables augmentation is required.
A: Snap in clip in a keystone jack prevents the keystone from dislodging from the wall plates and the patch panels. This feature provides enhanced connection and prevents disconnection which may occur in the course of ensuring powered supply to the target devices.
A: Surface mount boxes are enclosures used to install keystone jacks and other unobtrusive connectors where wiring within the walls cannot be done. Such surface closures are used to terminate network wires especially in desktops or walls where there is a need for the wires to be clean and tidy.
A: Strain relief in cable installations is used to eliminate physical force applied to the cable connections for risk of breaking or disconnections from each other. Often, the strain relief feature is integrated into keystone jacks and connectors as an arrangement where wires are restrained from strain.
A: UTP keystone jacks are a great tool for cabling systems since most people opt for Ethernet cabling. They are made up of unshielded twisted pair cables. They are different from other keystone jacks in that regard, as most standard networks do not require any extra shielding, which makes UTP keystones a more affordable option.
A: The junctions made from keystone connectors and wall plates tangents can cause issues but only if the specific ports are not being used on the wall plates. So, the easiest fix to use to offset the negative is to stick to using the standard keystone size. The majority of keystone jacks have a universal design.