The networking technology industry keeps changing rapidly; hence, every installation must seek reasonable, reliable cabling solutions. One such option is the Foil Twisted Pair (FTP) cable, which offers the advantages of twisted pair technology with an extra layer. In this paper, the authors wish to identify the particular characteristics of these innovative types of cables – FTP- and compare them to what is currently available in other ethernet cables, their respective functions, and what makes them suitable for different network environments. Readers can learn how users may enhance different performance indicators with the help of FPT cables in modern communication systems and simultaneously overcome the challenges of interference.
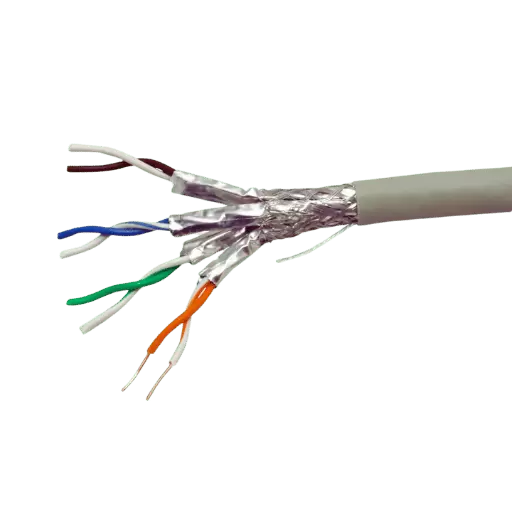
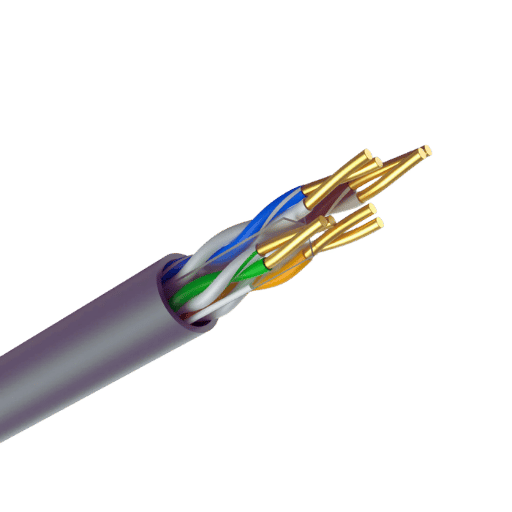
The Foil Twisted Pair (FTP) type of network cabling comprises pairs of insulated wires twisted together and has an outer insulator made of foil. The primary function of an FTP cable is to ensure that data is conveyed with a significant amount of electromagnetic interference (EI) and still a very high bandwidth capacity. Foil shielding prevents external noise from interfering with the signal carried by the twisted pairs and crosstalk between the pairs, thus making FTP cables ideal for areas with higher electrical noise. Therefore, since potential interferences in the signal quality are well handled using an FTP cable, the networking component’s success affects many applications, including LAN interconnections in data centers.
Foil Twisted Pair (FTP) cables reveal that they are different from Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) cables, mainly concerning the cable shield used and its performance parameters. UTP is completely unshielded and thus is prone to EMI and crosstalk, which lowers the utility of UTP in a noisy environment. On the other hand, STP wires have a further layer of shielding enclosing each wire pair, protecting them from electromagnetic interference. Unfortunately, the cost and weight of STP wires make them much bulkier and more expensive than both UTP and FTP parts. They tether these two extremes by using a foil cover for all twisted pairs that prohibits a certain degree of interference yet ensures that signals get transmitted without loss. This allows for personalization of the wires to where wire cost-effectiveness maintenance is also a key feature, thus making it possible for wiring technologies to be used between UTP and STP cables at varying networking requirements.
Foil twisted pair (FTP) contains various properties that further improve its efficiency, especially during data transmission. To begin, within the Foil Twisted Cables, the inclusion of foil shielding assists in preventing interference from external sources and reducing the crosstalk regarding the pairs; this is quite fundamental when the environment is crowded with cables, and signal interference is much more likely. Furthermore, compared to UTP cables, they usually exhibit a lower attenuation rate, which leads to better signal quality over longer distances. They are tacky and entail adequate structure that enables them to function appropriately in diversified networking settings, for instance, in the office or the factory. They also meet the cost-benefit regarding the businesses’ operation, defining FTP rather than UTP and category 6 or 6 A. Lastly, they are usually standard compliant, thus capable of most of the networking devices in the market.
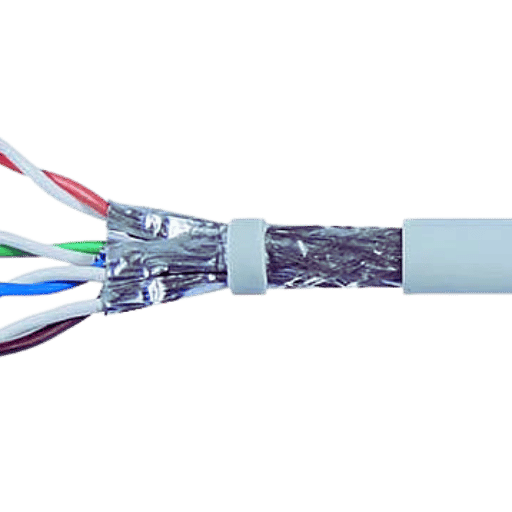
Foil Twisted Pair (FTP) Type cables are essential for the efficient and effective transmission of data in Ethernet networks. They are especially effective in minimizing cross-talk. Since such areas are densely populated, assimilating copper wire sheath around the twisted pairs is necessary. Consequently, cleaner signals are achieved, allowing faster transmission, especially with higher equipment deployments in virtually the same spaces.
Further, as data packets are being transmitted through the twisted pairs, the structure of the FTP cable allows for more excellent sycophantic cancellation of crosstalk, which makes it more effective. For that matter, it is evident that the FTP cables are mainly intended for use where there is a need to ensure steady and secure data transmission, such as telephone networks, video over IP, or fast internet services. In addition, they cater to the appetite for an increase in bandwidth in business environments, making them more favorable options in most current infrastructures together with cat5e and cat6a cables.
The performance of Foil Twisted Pair (FTP) cables in the network configuration is primarily determined by their structure, the effectiveness of the shielding, and the conditions where they are used. The studies reviewed have observed that FTP cabling performs better in attenuation and signal degradation than unshielded counterparts. This is because the cardboard covering provides insulation against external disturbance and crosstalk interference from nearby cables, enhancing the quality of any data sent.
In most network deployments, the ‘Category 5’ FTP cables offer data rates of 1 Gbps over 100 meters, performing well in standard Gigabit Ethernet applications. Furthermore, with the existing thick electronic apparatus in Industrial environments with heavy EMI, the benefits of the FTP cables become even more advantageous. Some models of the FTP cables also enable power over Ethernet or PoE capabilities, allowing the interconnection and control of data devices like IP cameras or wireless access points. All in all, the parameters of the quoted ISP cabling today will enable us to consider it a reliable tool for companies focused on constructing an effective computing network.
Foil Twisted Pair (FTP) cables are superior to other cables like Unshielded Twisted Pair (UTP) and Shielded Twisted Pair (STP) cables in key aspects, including shielding, performance, and intended use. UTP zip cords and STP cables have features that are equalized by employing foil shields against EMI to maintain the thin and large structure of the UTP dap even more. Thus, in those areas where interference is an issue, their performance is better than that of plain UTP cables, which are devoid of shielding.
On the other hand, STP cables are more expensive and bulkier than UTP cables, though they incorporate pair shielding. There might be no justification for using STP or FTP for low-interference level enclosures because UTP will be cheaper and still perform quite well. Nevertheless, in high-performance networks such as datacom installations away from other heavy electrical equipment, FTP has been seen to provide better performance than UTP or STP in signal and data transfer. In short, the type of cable to be used depends on the working environment, available budget, and the desired performance level, where more balanced wires, such as FTP cables with irritating fewer transmission factors, will enhance the data speeds.
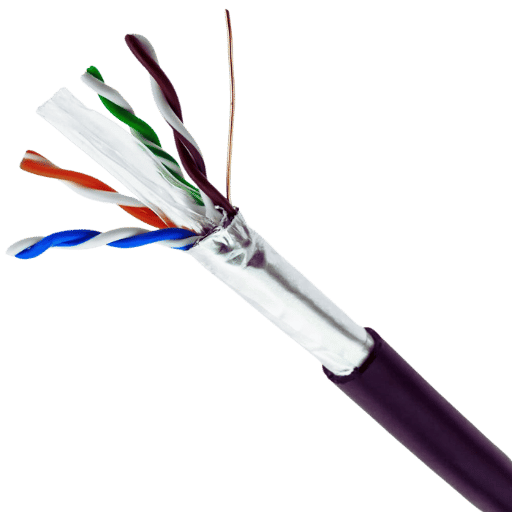

If you remember, FTP cables have special tape close to the socket jack. Cables used for FTP connections have specific characteristics that help restrict and eliminate electromagnetic interference (EMI). The foil enclosing FTP cables is a device that prevents external electromagnetic interferences from being absorbed by the cables and the signals induced by the wires themselves. This is typically helpful in places with electrical noise, usually in commercial settings or telecommunication centers packed with electronic apparatus. It is stated that this high level of shielding should ensure that data is transmitted with much reduced errors due to crosstalk, making it possible to use FTP cables under challenging network conditions. Also, using FTP cables may lead to reduced charges in time and an increase in the volume of throughput, which are crucial characteristics of data-intensive applications and communications.
Thanks to the design and shielding properties, the FTP cables help enhance the data transmission quality. The foil not only prevents EMI but also reduces the interpair interference of the twisted pairs, which improves the signal. In the opinion of such professionals, it follows that errors in the transmission process are minimized, and the quality of data is enhanced, more so in the case of high frequencies. Plus, because of additional shielded elements in construction, FTP cables can have larger bandwidths than the unshielded ones, thus helping keep up with the current fast-paced network environment. It is evident from websites such as Cable Matters and Belden that proper shielding and the configuration of the twisted pairs make it possible for the FTP cables to perform efficiently over longer distances, which is a plus for industrial and home applications where reliable services are required.
FTP cables incorporate materials that not only increase their strength but also their presence and, therefore, allow them to be used in different environments. The outer sheath in which the cables are encased is often made from high-grade PVC or LSZH material that helps prevent smudges, blistering, weather-environment, and chemical damage. Citing some of the articles available on the internet, such as on Anixter, it has been shown that such durable construction of the FTP cables makes them resist wear and tear, thus enhancing their usability for an extended period. In addition, articles from other industry players like Belden say that, if properly installed, the FTP cables can perform their function for over 20 years while resisting environmental elements such as high temperatures and humidity. This characteristic limits the frequency of replacements and guarantees that the network remains reliable throughout; thus, they are well worth it for both commercial and residential purposes.
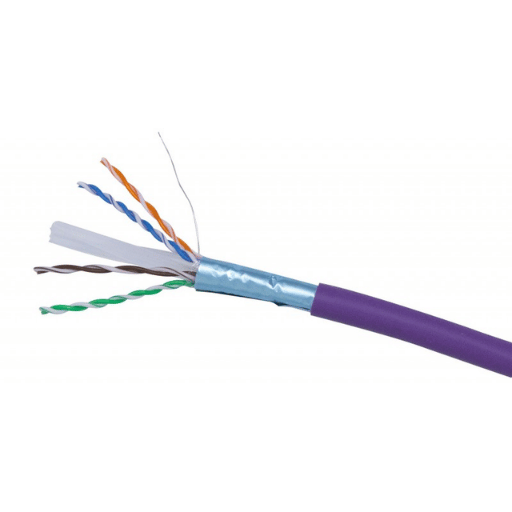
When inspecting FTP (Foil Twisted Pair) and UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) cabling, several striking comparative factors can significantly affect the choice of cables for particular needs.
To conclude, the decision to use FTP or UTP cables should be determined by how the cable installation will be used, the realism of its geographical location, the speed of data transmission needed, and the probable spending plan if several cable options are compared.
Due to their construction and better performance parameters, FTP cables are usually recommended in several cases:
Under these circumstances, the expenses involved in acquiring the FTP cables become worthwhile, owing to their increased efficiency and effectiveness, especially in the high-segment market.
Cost comparison of FTP (Foiled Twisted Pair) and UTP (Unshielded Twisted Pair) cables is never easy. Typically, UTP cables are cheaper because they lack metallic foiling, which makes them easily available for regular networking requirements. Though the initial cost of UTP cables is less than that of other types of cables, it can seem deceptive when it comes to the total cost of ownership many years into the future.
On the other hand, FTP cable costs are often higher because of the additional mechanical protection that helps control external interference and crosstalk, making it more appropriate for high-end networks. In-depth analysis and insights from reputable industry reports show that although UTP is sufficient in low interference environments, the durability and performance of the functioning wet-nylon FlexShield™ pipes in extreme environments can prove the high initial outlay worthwhile. This can result in lower recurring market costs and superior efficiency, especially in high-density or industrial situations.
Ultimately, the choice concerning FTP and UTP cables does not focus on basic expenses for acquiring UTP cables. Still, it is targeted towards identifying the particular network environment in which the wires shall be used and the possible costs expected of damaging or degrading them due to signal loss. This integrated approach assists in ensuring that organizations are making the right investments in networking connectivity.
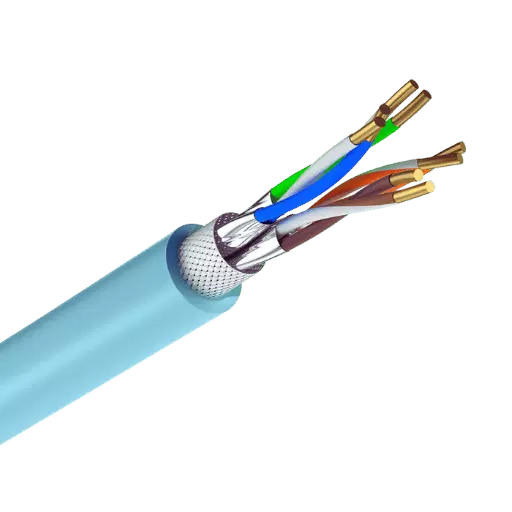
Cat6 FTP cables are another enhancement in the networking field that solves the problem of higher data rates and cross-talk interference. The most noticeable advantage of Cat6 FTP cables is the shielding, which protects these wires within the twisted pairs, thus preventing EMI and internal crosstalk, which is beneficial for signal quality improvement.
These cables are rated for data transfer speeds of 10 Gbps up to 55 meters in length. Such speeds make the cables usable for high-speed environments such as data centers and enterprise networks. In addition, less crosstalk leads to better signals and effective communication, which is essential in areas with a lot of cabling or electronic interference.
Moreover, the previous generation of Cat6 FTP cables is backward compatible, so joining with existing network systems is no issue. These countless advantages and their functionality make Cat6 FTP cables an option that most organizations looking to perfect their networking system and keep pace with future requirements very comfortably prefer.
The term 23 AWG (American wire gauge) specifications indicate the use of the diameter of the wire that is to be used in the ethernet cables, more specifically 23-gauged wires, which are the standard for a Cat six and other recent cables. For further understanding, the 23 AWG specification is good for FTP cables because it represents a compromise between flexibility and signal loss, achieving much longer ranges without compromise in quality.
When arranging the wires in a standard FTP cabling system, four pairs of twisted wires are used, which is the case with shielded twisted pair construction. The kablenet central conductor also aids the current transmission by providing insulation, and each twisted wire pair utilizes internal current transmission. WYMAX installation will involve a very high data rate of up to 10 Mbps. This ensures that the cabling is efficient and supports high-speed data transmission rates of up to 10Gbps over a distance of 55 meters when installed in high-density spaces. The four-pair configuration not only optimizes performance but also conforms to other operating standards, making it suitable for current networking technology.
The importance of cable shielding is particularly evident in networking cables used in areas with EM interference, where it is absolutely necessary to preserve the signal quality as much as possible. STP cables possess added shielding materials, such as foil or braided copper, that help reduce external interference and boost performance. However, using shielding materials is also beneficial for reducing crosstalk and improving the SNR, which increases the chances of successful communication.
Many times, the performance of the shielding is relative to the type on which the treated surfaces have been used or the kind of treatment scheme employed, whether a common sheath is utilized over the whole cable or separate sheaths for pairs. As such, the performance of cable modem networks that employ shield cables is very good with a lower ber and higher speed, even in congested environments or active electrical regions. Therefore, in areas where such businesses are undertaken, it is reasonable to provide good server twisted pair cables that are relatively appreciating and improving network performance.
Following these recommendations will improve the functionality of FTP Ethernet cables and make them more efficient and durable under conditions of overcrowded local networking.
Prudent prevention and response to some of these problems must be carried out to maximize the network’s reliability and performance.
Preventive maintenance is a requirement if you want ftp ethernet cables to serve their purpose of long service and stellar performance characteristics. First, the inspections must cover every routine task done on the cable for any indications of deterioration like cuts, fraying, or insulation failure. Keeping the wires neat and unencumbered is also advisable to avoid harsh treatments that come with movement or being knocked by heavy articles.
Atmospheric control of temperature and humidity should also be practiced to prevent unwanted environmental conditions, which can eventually degrade some of the cable materials. The contact surfaces of any connector must be cleaned from time to time, and any other ends of the cable must be exposed so that the volume of dust on or around them is minimal.
Along these lines, networks and systems need to be physically changed and refreshed so that any new technological improvements and software upgrades can be accommodated because old systems has a physical degradation factor related to the performance of the cable. Adopting these maintenance strategies will ensure that the ftp ethernet ecosystem remains as efficient as possible and also increases its lifetime.
A: In telecommunication, Foil twisted pair or FTP cable is a type of Ethernet Network cable that has twisted pairs surrounded by a foil shield to prevent the cables from electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk, what UTP lacks in comparison with other types of cables.
A: The main difference between UTP and FTP cabling is that while the MPEG, which is usually high-frequency encoding of the interlaced passive band, involves the use of two wires, FTP wiring is centric and incorporates a foil, which aids in minimizing EMI; FAQs explanation, and crosstalk.
A: Compared with unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cables, FTP cables provide greater resistance to EMI and crosstalk interference effects. Thus, they can be used in places with a lot of electromagnetic noise or for high-speed data transmission.
A: Yes, FTP cables can be used for home applications, especially when appliances can be sources of electromagnetic interference. Such cables perform better than UTP alternatives. They also mitigate EMI and crosstalk better than UTP wired connections, ensuring more dependable and stable network effectiveness.
A: The principal difference is that although Kodi’s cables are a composite of foil and an enclosing plastic of the type commonly incorporated into U/FTP, U/SFTP cables have one inner Foil in addition to the braiding other than only plastics.
A: The discussion should center on satisfying a specific requirement rather than searching for an inclusive logical improvement. Cat6 is a class of proprietary cables for computer networks that are available with and without shielding, whereas FTP is only regarding shielding requirements. High-speed F-type connectors are being attached to dual-purpose FTP Cat 6 cables.
A: The construction and arrangement of cables impede transmitting signals. For instance, the design and construction of the FTP cables enable enhanced data transmission where good shielding is necessary.
A: Yes, utilizing FTP connectors for Patch Cables is suitable. They are meant for Ethernet cabling and can interconnect equipment in a network while providing reliable connections with the norm, EMI, and cross-handling.
A: FTP cables are intended for telecommunication rooms, industry and development centers, and other sites with high EMI levels. The foil shielding further minimizes EMI and crosstalk to transmit data properly.
A: A foil shield in an FTP cable provides an extra layer of protection against EMI and interference, which leads to better stability of the cable system due to less interference from outside factors.