Fiber optic connectors are vital in achieving efficient and dependable data transmission in telecoms and data communications. This is among many types of fiber optic connectors that are widely used because of their versatile nature. The main objective of this article is to give an overall view of SC Connectors and other general information related to Fiber Optic Connectors, such as their functions, types, applications, etcetera. Technical understanding and advantages of these devices will help individuals know more about how they work together for the smooth running of present-day communication systems. Suppose you have just started working with fibers or are an experienced professional looking forward to broadening your understanding of them. In that case, this manual will act as a good reference point for you.
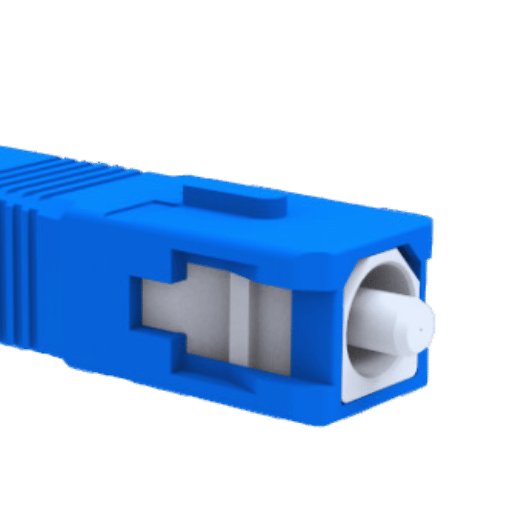
Subscriber Connectors, or SC connectors, are optical fiber connectors that help establish fast connections by using a push-pull mechanism. It has a 2.5mm ferrule and is characterized by its high accuracy and low insertion loss, which makes it perfect for use in high-performance networks. The design of SC connectors guarantees consistent performance over time via robust connections where alignment is always maintained through durable interfaces. This type of connector has been standardized to ensure convenience as well as compatibility; thus, it is widely used within telecommunication systems due to its ability to withstand harsh conditions alongside efficient signal transmission capabilities during data transfer applications.
SC connectors in a network work by establishing a precise and safe connection between fiber optic cables and network devices. The use of a ceramic ferrule to align the fibers accurately minimizes signal loss while enhancing effective transmission. SC connectors have push-pull functionality that supports fast, reliable connection/disconnection, thus being suitable for areas with many moves. After joining together, the SC connectors maintain stability because they are designed to be strong, thereby ensuring that signals remain intact even in high-density network installations.
According to their design, efficiency, and ease of use, SC fiber connectors are compared with other types of connectors. They have a 2.5mm ferrule which makes them bigger than LC connectors that have 1.25mm ferrules; as such, they create stronger links for diverse uses. Unlike the push-pull mechanism used by SC connectors during the engagement and disengagement stages, ST connectors employ a bayonet-style coupling mechanism that takes more time to connect or disconnect because it involves twisting motions. On the other hand, FC connectors are stable in high-vibration environments due to their threaded coupling mechanisms, but this makes them complicated when one wants to connect or disconnect cables since there must be rotations made while aligning holes between two sides involved in the connecting process, unlike easy-to-do push-pull style applied by sc connector which only requires pushing forward until the latch clicks into place. Generally known for being robust yet lightweight at the same time, with low insertion loss and durability factors, SC connectors have been widely adopted within various networking fields using optical fibers compared to any other type of connector.

When examining fiber connectors, it is important to differentiate between single mode and multimode fiber connectors as they have different uses and offer different benefits based on the requirements of a particular application.
Connectors for Single Mode Fiber:
Connectors for Multimode Fiber:
To sum it up, when you need high bandwidth or long distance connectivity with low losses, then you should use single-mode fiber connectors, while multi-mode fiber connectors are cheaper options for short-range connections where sufficient local area network bandwidth is required within most enterprise environments. It takes both types into consideration if one wants an efficient optical network since each type supports different operational needs and performance criteria.
When deciding between SC, LC, or other fiber connectors, a number of important considerations should be made:
Connector Type and Form Factor:
Application Specific Requirements:
Performance And Standardization:
In conclusion it is dependent upon what exactly one needs from their network; physically limited areas , desired performance levels or even costs implications therefore evaluating all these factors will lead unto best selection thus enhancing efficient & reliable communication over optic fibers.
Different fiber optic cables have been designed to cater for different telecommunication and data transmission needs. Below are the main types:
Single Mode Fiber (SMF):
Multimode Fiber (MMF) OM1:
Armored Fiber Cable:
The choice of what kind of fiber cable should be used depends on specific application needs including distance, bandwidth requirements and environmental factors involved; failure to do this may lead to poor network performance hence reduced lifespan.

Materials and Equipment
Step 1 – Preparing The Fiber
Step 2 – Cleaving The Fiber
Step 3 – Preparing The Connector
Step 4 – Crimping The Connector
Step 5 – Polishing The Connector
Step 6 – Inspecting Fiber End
Step 7 – Testing The Connector
SC connectors must be correctly installed in order to maintain efficient network operation and ensure minimum signal loss, therefore it is important that each step is followed precisely.
Fiber patch cables maintenance involve several important practices to achieve the best performance and longevity. These are some of the tips that will help in maintaining them effectively.
Maintain your fiber optic network reliability and efficiency through this kind of maintenance.
Dirty Connectors
Connectors Out of Alignment
Physical Damage
These common troubles should be solved by cleaning properly, aligning carefully, and checking frequently, thus greatly improving network performance.

Connector end face geometry
Return loss
Application
In conclusion, SC/PC connectors are best for general optical fiber uses due to their flat end faces and lower return losses while SC/APCs with an eight degree tilt on the tip have got higher returns losses making them ideal for precise or high bandwidth applications employing sc fiber optic cable connectors hence both can be utilized.
The SC APC optic fiber quick connector is used when it is necessary to minimize back reflection, thus achieving stability of a high-performance network. Here are some of the main areas of its application:
The utilization of network systems with these components significantly improves performance and reliability thus meeting the demanding needs brought about by current telecommunication infrastructures.
SC UPC (Ultra Physical Contact) connectors have several benefits for network installations, which is why they are widely used in different communication technologies.
By using SC UPC connections during installation processes, companies can create systems that are not only efficient but also reliable, as well as affordable enough to meet all needs posed by current-day communication systems.

Fiber optic fast connectors are pre-terminated connectors that can be installed in the field and offer a rapid way to terminate fiber optic cables. This reduces installation time dramatically while still maintaining good numbers for insertion loss and return loss. Fast connectors come in several types, such as SC, LC, or ST, which are chosen depending on the needs of certain networks or their configuration. They make possible easy integration into already existing fiber optic networks so that they can be quickly put into operation thus increasing efficiency in dynamic telecommunication environments.
Butterfly fiber optic cables, also called flat drop cables, are becoming more popular in the fiber optics industry because they are flexible and easy to install, especially when used with Unicam connectors. These cords generally contain one mode of fiber that is enclosed in a strong external jacket, which is flat shaped, hence tough and resistant to many environmental factors. The design also makes them easily laid on surfaces and facilitates transitions from outdoor to indoor applications, making them perfect for fiber-to-the-home (FTTH) uses. Furthermore, butterfly fiber cables have increased crush resistance and tensile strength which ensures that they can last longer and work reliably across different deployment scenarios. Therefore, this makes such types of wires the best choice for network operators who want to achieve maximum performance together with high installation density within cities.
The future of optical fiber connectivity seems to be very bright because of the rising demand for higher bandwidth and new technologies. One such technology that has shown promise is artificial intelligence (AI) coupled with machine learning (ML) which can greatly improve predictive maintenance as well as network management systems. With these tools at their disposal, administrators will be able to detect potential problems before they occur, thereby minimizing downtime and enhancing reliability across networks.
Another high potential area lies in quantum fiber optics development that seeks to utilize quantum computing power for creation of secure channels through which information may travel undetected by any eavesdropper. This could prove especially important in industries like finance or government where the need for strong data protection cannot be overemphasized.
Additionally, bend insensitive fibers together with OM3 technology advancements are likely going change how we deploy cables in difficult terrains forever. They have been built so that they can still work even when twisted or bent hence reducing signal loss during installation process while at same time giving more flexibility on where one wants them installed.
Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) is another key area that needs continuous improvement if we are to keep up with growing demand volumes; it allows more than one data channel to use a single fiber optic cable simultaneously, thereby increasing transmission capacity without necessarily requiring extra infrastructure investment.
In conclusion, smarter networks, security beyond ordinary comprehension levels, flexibility never imagined possible before concerning fibers and greater data transfer speeds than ever thought achievable are some things we should expect from our optical fibres going forward so as meet various global needs in terms scalability among others.
A: It is a standard connector type most commonly used in network applications. This one uses a push-pull coupling mechanism, which makes it connect and disconnect easily. It is usually used in singlemode as well as multimode fiber optic networks.
A: In this case, simplex fiber optic cables have one fiber, so they are good for transmitting data only in one way. On the other hand, duplex ones contain two fibers within a single cable, enabling bidirectional data transmission. For simultaneous two-way communication, you often find duplex SC connectors being used.
A: Mechanical connectors align and join the ends of two optical fibers together using a mechanical fixture and index-matching gel. A quick, reliable connection can be achieved with these connectors without fusion splicing tools or equipment, especially for single-mode mechanical connector types.
A: Single mode fibers have smaller core diameters and can transmit data over longer distances with less signal loss than multimode such as OM1. They work best for high-speed data communications and telecommunications, like FTTH (Fiber to the Home) and CATV (Cable Television).
A: The LC connector has a smaller size than the SC connector, plus it uses a latching mechanism, thus suitable for high-density applications, whereas on the other hand, the sc connector is larger in size and uses a push-pull design, which offers ease of use. Both can be employed across various applications, including but not limited to singlemode and multimode networks.
A: An adapter connects two fiber optic connectors so light can pass through them without interruption. They can be LC, SC, or hybrid, and they are important for keeping the fiber link intact.
A: Fiber reusable connectors allow for re-termination many times over, thereby bringing about cost savings and installation and maintenance flexibility. These types of connectors are common in situations where fast field connections are needed.
A: Fast or fiber-fast connectors allow speedy terminations of fiber optic cables without any special tools. They find extensive applications in FTTH installations and data centers, among other areas that require quick deployments.
A: A pigtail refers to a short length of optical fiber cable with one end terminated with a connector while the other has exposed fibers. It helps establish permanent connections between optical fibers and network component connectorized fibers, thus simplifying terminating these fibers.
A: Yes, you can connect single-mode fiber to multimode fiber, but it’s not recommended because they have different core diameters and light propagation modes, which makes direct connections result in significant signal loss and performance degradation.