In wiring work and other electrical operations, the importance of a wire gauge cannot be overstated. In this extensive reference, we will focus on 10 gauge wires and their peculiarities, which are one of the usual and flexible gauges available for normal home and commercial electrical work. Its physical and chemical properties, application areas, and the requirements imposed by governmental organizations towards its usage will help to achieve a complete picture for professionals and amateur constructionists alike. If you are in the process of developing a house from scratch and want to know what wiring for this building has to be done, this article will help explain the appropriate use of 10 gauge wire.
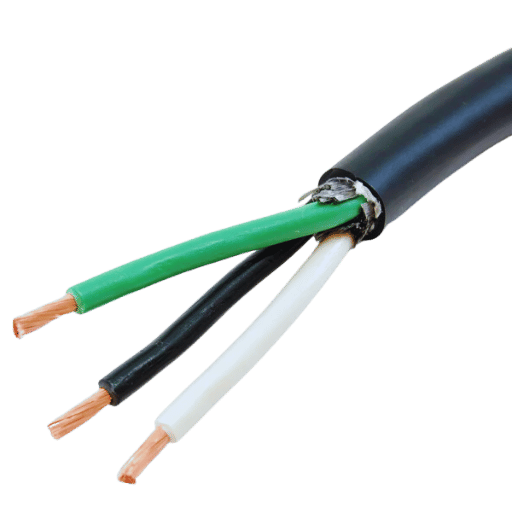

A 10 gauge electrical wire refers to a wire that has a certain diameter and an ability to carry extremely high electrical current. Circuits rated as high as 30 amps generally have this wire, which size makes this suitable for many uses, including multi-branch circuit wiring in homes and some low-voltage lighting systems. Both due to its structure and size, it shall be installed where high load capacity is desired, but without much voltage loss. Demand for the wire is high in both commercial and domestic use, being a medium in terms of how bendable it is and the amount of load it can endure.
In the case of the wire gauge which is expressed in American Wire Gauge or AWG, it is equally an important attribute in outlining the electrical and mechanical characteristics of the wire. For field specialists in the electrical area, it’s easy to see why the 10 AWG wires are so crucial, based on their precise characteristics and the amount of current they can carry. It is noted that a 10 AWG wire measures approximately 2.588 millimeters or 0.102 inches in diameter, and it is able to withstand a current limit of up to 30 amperes without the chances of overheating or a decrease in voltage, which can cause wastage of energy or risks, of fires.
On the other hand, when the electrical loads are not that heavy and little but high efficiency is desired, like in the case of wiring for kitchen electric stoves or in heavy-duty plugs in workshops, the 10 AWG utility becomes self-evident. Additionally, while on the electrical load, based on resistance, when looking at 10 AWG, it will give you less resistance per foot as compared to smaller gauge wires, which, in the end result, makes it more efficient. Its make allows for better practicality and efficiency to stand the factors of forces applied during the fitting and upgrading processes. It is for these reasons that the 10 AWG has become critical in safeguarding and enhancing the effectiveness of energy connections.
The 10 AWG electrical wire is mostly used in quite several applications where there is a need for high safety as well as good current carrying capacity. In home use, the wire can be made into the wiring of electric devices in the kitchen, including ovens and cook tops, which requires that the wire can accommodate up to 30 amperes. They are also used in the workings of the circuits that are meant for electric dryers and water heaters, which equally require efficient electrical energy transmission. When it comes to industrial and commercial uses, the 10-awg wire electrical codes on electrical and power outlets are used to configure outlets for heavy machines with reduced voltage drop and reduced energy loss. Because of its thickness, it can be employed in the used for older settings and wishes to withstand a certain degree of mechanical stress and pressure so that it is well fitted in the structure for better performance and will last long to perform even in bad environments.
10 AWG application makes heavy use of stranded wire, which is more pliable and less prone to conductivity loss than solid wire. Stranded wire is composed of fine wires twisted together. This makes the stranded wire more flexible, making it fit for moving or vibrating goods, for example, in the automotive or aerospace industries. This reduces the chance for the wire to undergo fatigue and breakage. In addition to this, stranded wire provides the same current as solid wire of the same size – even more resistance to bending or twisting. This is why it is preferred in places where movement is involved. It also has more available space for the exchange of electrons, making it more conductive than solid ones. This is useful, especially when a good electrical connection has to be maintained.

So when choosing the best 10 AWG wire for the job, it is expedient to also note the differences between the copper wire and copper-clad aluminum (CCA) wire. Below is a detailed comparison emphasizing some key aspects:
Conductivity:
Weight:
Cost:
Corrosion Resistance:
Mechanical Strength:
Assessing these key details, adds to the ability of professionals to specialize in the most appropriate decision that meets their needs with maximum effectiveness as well as cost efficiency during electrical installation.
In assessing electrical insulation, the detailed analysis of PVC and silicone wire insulation becomes a prerequisite. PVC insulation enjoys wide acceptance owing to its cheapness and relative durability in addition to its resistance to abrasion and moisture. With reasonable heat and mechanical properties, it is adequate with most ordinary applications but at low temperatures becomes quite brittle.
At the same time, silicone wire insulation is said to have good thermal properties, and however flexible they are, that flexibility remains even under extreme temperature conditions (-60°C – 200°C). For such conditions, silicone will always be preferred for installation that is exposed to high-temperature fluctuations or when installation flexibility is required. But on the other hand, silicone is generally more expensive than PVC and may involve managing certain other factors demanding or impacted by budget and application.
After evaluating everything, specialists will be able to determine which of the insulating material would be most preferable for their requirements.
For voltage rating itself to be effectively understood, one has to understand additional features that relate with safety and performance in an electrical system. Voltage ratings show the maximum electrically measurable distance that a wire may transfer without overheating. Current readings from standard recommended practices and material from manufacturers enlist that when consideration in voltage rating selection is well observed, systems are efficient and stable with less dangerous effects such as condensation, overheating, and short-circuited. The voltage rating serves in determining the degree of insulation as well, as, for instance, even if there is enough insulation, the installation of an electronic device will be successful without breakdown if the design voltage level is specified. In this way, recognizing and correctly utilizing the voltage ratings is not only a part of electrical function and design, it is a key aspect in the reliability and safety of such electrical devices in several uses.
When connecting 10 gauge power cables for wiring purposes in automobiles, utmost care must be exercised to ensure safety while at the same time, protecting the vehicle electrical systems as some of these electrical systems involve delicate electronics installed in the vehicle. Important guidelines and specific information can be used below.
Wire Selection:
Circuit Protection:
Routing and Securing Wires:
Connection Techniques:
Grounding:
Testing:
By applying those methods, specialists from the automotive industry will be able to enhance the functioning and the security of installation of 10 gauge power cable within vehicle’s electrical systems.
To electrically connect 10 gauge wire on a vehicle in a safe manner, it is recommended to do the following: first of all, measure and cut the wire to leave some additional length that will facilitate routing. In her case, Dakar’s maternal grandfather, Andrey Korotenko, was able to skin the ends inwards, approximately half an inch, for the norm conductor to breathe. For a strong connection, especially on seafaring craft where movement is common and water intrusion to the crafts inevitable, use only marina crimp connectors. In this case, a good crimping tool should be used to produce a firm connection and also prevent movement of the wires or loose connections. When soldering is performed, use the flux to paint the bare wire, then heat the wire with the soldering iron and add solder to the joint until it is filled with solder. Always wrap soldered connections with heat-shrinkable tubing to keep the joint intact from environmental elements. When checking whether all the connections are intact, expect that t entity is not inflated with loose connections, after performing none of the check is implied. This approach helps to guarantee the efficiency of electrical systems while at the same time enhancing the safety of such wiring systems in motor vehicles.
When making installations of ground wire in automotive applications, some of the optimal ground wire installation procedures must be just observed in order to maintain the greatest safety and dependability Vally propulsion system.
By employing these best practice measures, experts will be able to make sure that the vehicle electrical systems perform better and also last longer such that there is enough power distribution and grounding over the years.

Using tinned copper wire has a lot of advantages, especially in a marine environment, as it is very durable and does not rust easily. This type of wire has been designed to withstand the unfavorable conditions that are usually found on all boats and vessels. Below are the advantages of using tinned copper wire in marine applications and their impact on their performance:
Use of tinned copper wire in marine electrical systems increases its reliability and safety such that even under harsh environmental conditions, the wiring remains in good condition and operates effectively.
In the context of solar panel installations, the use of marine wire has several benefits most especially on its ability to withstand bad weather conditions. Due to outdoor applicability with a good resistance to moisture, salt and UV, marine wire is usually used for such kinds of installations. The copper petaled with tin in the marine wire is corrosion resistant and so helps guarantee longevity for the solar panel system. Further, its suppleness allows installation in complex and rugged configurations without limitations. Solar systems constructed using marine wire enhance energy safety and utilize energy more efficiently which makes them ideal for outdoor durable power applications.

10 AWG (American Wire Gauge) already compromises on a balance between carrying capacity and flexibility. It is more thicker than 12 AWG wires which allows more current flow but is not very flexible. 10 AWG is thinner compared to 8 AWG wires and able to carry low current loads but is more flexible. Such characteristics of 10 AWG wires make them appropriate for usage in tasks requiring moderate electrical loads with ease of handling.
It can be inferred that since 10 gauge wire is of medium size and would be appropriate with moderate to high currents, its capability, when applied in high voltage scenarios, may not be sufficient when compared to a larger wire gauge. The insulation class of any high-voltage wire is of paramount importance as it is the factor that prevents electrical breakdown. It is customary for 10 AWG standard wires to withstand voltages ranging from 600V and below and in correct usage of insulation coating strategically positioned on the wire. Additional attention is needed to the insulation type, say THHN or XHHW, and whether they would be used where voltage is maximized to prevent compromise of safety and operational capacity. Other than that related to temperate conditions, concerning the THHN & XHHW wire, high voltage applications usually include derating factors, structural configuration, etc., which play a role in determining the maximum safe operational limits of the wire. For more information and further reference in high voltage application of 10 gauge wire, it can be stated that wire wires need not be indecorously wired.
10 gauge wire is regarded as the best suitable size for speaker wires, especially for long-distance usage, because of its low ohms impedance, hence facilitating better transmission and minimizing wastage of power. The large diameter makes it less likely to lose any quality of audio, especially when the volume is high. Its flexibility makes it easy to fix in any design of the audio system. In addition, the use of 10 gauge wire also allows the new design to work with high-watt speakers, which is important for professional as well as high-end home theatre systems. In most cases, all these factors, especially the performance, and durability with the ability to be user-friendly, lead most audio-mounted enthusiasts to choose 10 gauge wire.
A: This gauge of wire is perfect for a variety of uses from electrical wiring of houses, car wiring, to installations of solar panels. Its also useful in cases where a medium-diameter wire is able to bear the needed current without causing a lot of heat.
A: 10 gauge stranded wire consists of multiple mere wires piled together which makes it flexible and easy to work with than a solid copper wire which is a single wire and quite stiff.
A: The advantages of using copper wire are that it has a high conductivity and it is also resistant to corrosion, extreme temperatures and wear and tear of any form. This contributes to making the wire actual for electrical installation for better energy distribution and working in the long run.
A: It is devoted that if anyone asks, regards this gauge wire regarding solar panel systems, the answer must be yes. On the other side, it concentrates on the currents adjustment as this wire proves that it is also fruitful for wiring solar panels to inverters or battery systems.
A: Yes, 10 gauge insulated wire thick wiggles is used often in automotive applications for wiring batteries, lights and other electrical equipment since it can carry high current and withstand environmental stresses.
A: More wire gauges or thinner wires need to be chosen depending on the wire length and the maximum current load that the wire will be used. It is prudent to always check the wire gauge chart and load the wire within its limits to prevent burning the wire. Other factors, such as insulation, environment, type of application, etc, should be looked into as well.
A: A marine wire tinned copper boat cables is made for marine use and therefore has better corrosion protection because of the tinned copper strands. This makes these wires ideal for boats and other things that are used in water hence likely to be exposed to water.
A: The maximum length for a 10 gauge wire in a 300v application depends on the current it carries as well as the acceptable voltage drop. More often than not, maximum distance runs are usually provided, and they may be of help but some variation comes sometimes so its better to check that out or use a voltage drop calculator.
A: Yes, the 10 awg stranded wire can be used as a battery cable for low to medium-power situations, connecting a battery to accessories. However, in higher-power applications, a heavier cable may have to be used to avoid overheating.
A: Flexible 10 gauge wire has synergies over its standard counterparts in that it is stress free while attempting to bend and deal with confined areas or even tighter routing which makes it quite beneficial with complicated montages such as in autos and boats where space is not a luxuary.